A Grid-Interactive Efficient Building (GEB) is an energy-efficient building that uses smart technologies and on-site distributed energy resources to provide demand flexibility while co-optimizing for energy cost, grid services, and occupant needs and preferences, in a continuous and integrated way.
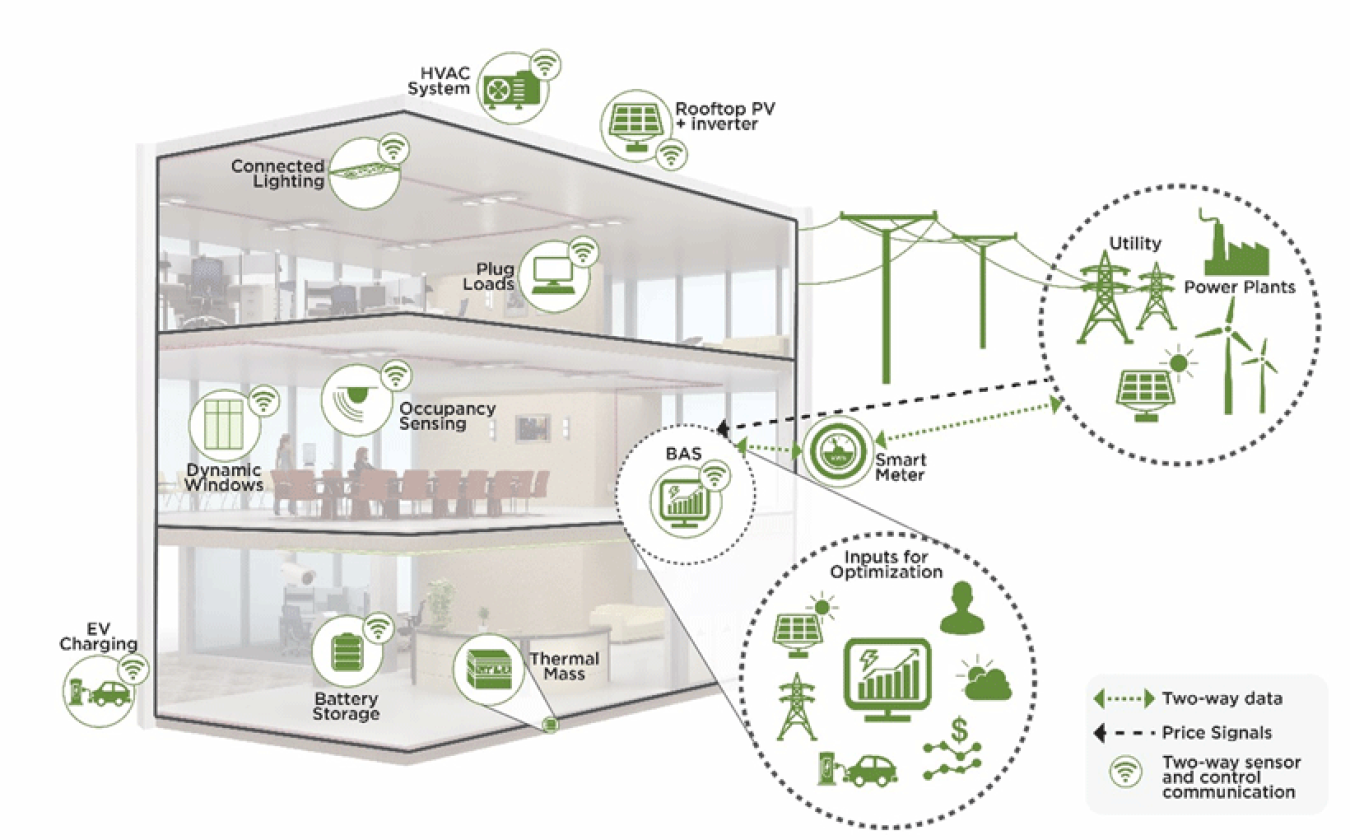
The Federal Energy Management Program (FEMP) plays a key role in helping agencies understand and meet energy-related goals, including those surrounding GEB. This support includes identifying, sharing, and demonstrating best practices among federal agencies, as well as providing technical support and developing tools and resources.
Federal Smart Buildings Accelerator Overview
As referenced in the Energy Act of 2020, FEMP supports the Federal Smart Buildings Accelerator (FSBA) to design and implement specific approaches that would accelerate the adoption of smart building and grid responsive technologies. This effort is building upon GEB research conducted in the U.S. Department of Energy Building Technologies Office (BTO) and the General Services Administration (GSA). The FSBA was introduced at Energy Exchange 2022 and concluded in September 2024.
FSBA Outcomes
The FSBA promoted smart buildings and GEB technologies across federal agencies, laying the groundwork for future advancements in energy efficiency. By providing education, technical assistance, and facility assessments, the FSBA helped agencies identify both opportunities and challenges in adopting GEB technologies. The FSBA highlights the ongoing need for continued education, funding, and technical support to ensure federal buildings can fully transition to energy-efficient, grid-interactive operations.
FEMP FSBA Resources
As part of the accelerator, FEMP developed resources to help federal agencies explore GEB technologies, benefits, and use cases.
Workbook
FEMP's Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings Strategies and Technologies Guidance Workbook helps building owners, energy managers, and facility managers prioritize potential grid-interactive strategies, technologies, and electrification and controls upgrades in federal and commercial buildings.
Technical Reports and Fact Sheets
The Key Grid-Interactive Building Technologies for Federal and Commercial Facilities report provides an overview of key GEB technologies and their potential for deployment in federal and commercial facilities.
The Guide for Grid-Interactive Buildings for Federal Agencies report provides an overview of GEB characteristics and benefits and how to analyze, identify, and implement GEB retrofit opportunities.
The Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings Support Federal Facility Decarbonization fact sheet describes how GEBs can enable demand flexibility that has the potential to reduce electrical infrastructure costs and transform the grid edge, where buildings connect to the power grid.
The Best Practices for Smart Grid-Interactive Efficient Building Ready Performance Contracts fact sheet provides steps for incorporating GEB energy conservation measures into performance contracts.
The Cybersecurity Considerations and Research Pathways for Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings fact sheet describes how interconnected systems and smart devices should be designed with cybersecurity best practices to prevent security gaps and potential attack paths.
The Best Practices for Resilience in Smart Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings fact sheet outlines processes and considerations to guide the design and operation of GEBs in ways that promote facility resilience.
Case Studies
Carl T. Hayden Veterans Affairs Medical Center: Smart Buildings Case Study
Key Characteristics of GEBs

Learn more about Electrification and Decarbonization Strategies for Federal Agencies.
GEB Decarbonization Benefits
GEBs decarbonize the building stock by utilizing:
- Energy efficient equipment to reduce energy usage
- Tight building envelopes to reduce heating/cooling energy use
- Renewable energy generation (e.g., PV panels, etc.) and energy storage to replace carbon heavy energy sources and enable fleet decarbonization
- Grid connected smart technology and energy storage to help integrate variable renewable energy sources on the grid and further replace carbon heavy sources
Demand Flexibility
Buildings can provide flexibility by reducing wasted energy, helping balance energy use during times of peak demand and/or plentiful renewable generation, and reducing the risk of frequency deviations.
As the grid becomes increasingly complex, demand flexibility can play an important role in helping maintain grid reliability, improving energy affordability, and integrating a variety of generation sources.
Additional GEB Resources
FEMP Publications
GSA Oklahoma City Federal Building: Smart Buildings Case Study demonstrates that GEB-ready strategies and technologies can be deployed across buildings with minimal investment.
BTO Technical Reports
This Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings Technical Report Series provides background information about GEB services and analyzes different areas of building technologies including HVAC, envelope, lighting, controls, and an overview of research challenges:
- Overview of Research Challenges and Gaps provides background information about GEBs and highlights key technologies along with their potential to provide grid services.
- Lighting and Electronics provides general description of lighting specific technologies and contains details about how the technologies provide grid services.
- Whole-Building Controls, Sensors, Modeling, and Analytics provides general description of controls specific technologies and contains details about how the technologies provide grid services.
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC); Water Heating; Appliances; and Refrigeration provides general description of HVAC specific technologies and contains details about how the technologies provide grid services.
- Windows and Opaque Envelope provides general description of envelope specific technologies and contains details about how the technologies provide grid services.
A National Roadmap for Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings announced BTO's national goal for GEBs: To triple the energy efficiency and demand flexibility of the buildings sector by 2030 relative to 2020 levels. The roadmap includes 14 key recommendations for a broad array of market and policy actors.
The Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings Projects Summary report provides background information and descriptions for ongoing and completed projects related to GEBs.
GSA Technical Reports
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and GSA Blueprint for Integrating Grid-Interactive Efficient Building Technologies into U.S. General Services Administration Performance Contracts report outlines a screening process that will enable GSA to narrow down sites across its large portfolio of buildings to a prioritized list of candidate sites with the greatest potential for cost-effective GEB implementation.
The Grid-Interactive Efficient Building Case Studies In the Federal Portfolio report provides examples of GEB technologies currently used in U.S. federal buildings.
NREL Technical Reports
The Exploring Grid-Interactive Efficient Building Strategies for Laboratories Through Energy Modeling report documents an analysis of GEB opportunities for reducing energy costs and emissions associated with laboratory operations.
RMI Reports
The Value Potential for Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings in the GSA Portfolio: A Cost-Benefit Analysis report provides insight into the analysis of GEB cost and energy savings.
The Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings Made Easy: A GSA Building Manager's Guide to Low- and No-Cost GEB Measures report provides an overview of grid-interactive efficient buildings and lays out actionable steps for GSA building managers to implement these no- and low-cost measures.
Utility Open Houses for Federal Customers

