The Fall 2020 newsletter about the DOE Wind Energy Technologies Office's R&D projects, accomplishments, upcoming events, and recent publications.
Wind Energy Technologies Office
October 12, 2020The biannual U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Wind Research and Development (R&D) Newsletter provides recent news about the DOE Wind Energy Technologies Office's R&D projects, news, accomplishments, and recent publications.
Letter from the Wind Energy Technologies Office Director, Dr. Robert C. Marlay
Although recent circumstances have introduced an economic pause in some sectors, the U.S. offshore wind industry continues its steady progress toward a robust energy future with several offshore wind projects and related supply-chain investments in various stages of development. The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Wind Energy Technologies Office (WETO) anticipates this future by focusing its attention on an array of high-priority research and development (R&D) needs, broadly categorized as advanced technology, siting and environmental challenges, and the integration of wind power at scale with the electric grid.
Current Research & Development
ExaWind Supercharges Wind Power Plant Simulations on Land and at Sea
Suite of open-source, HPC-powered physics codes allows engineers to do everything but collect their mail inside a virtual wind power plant
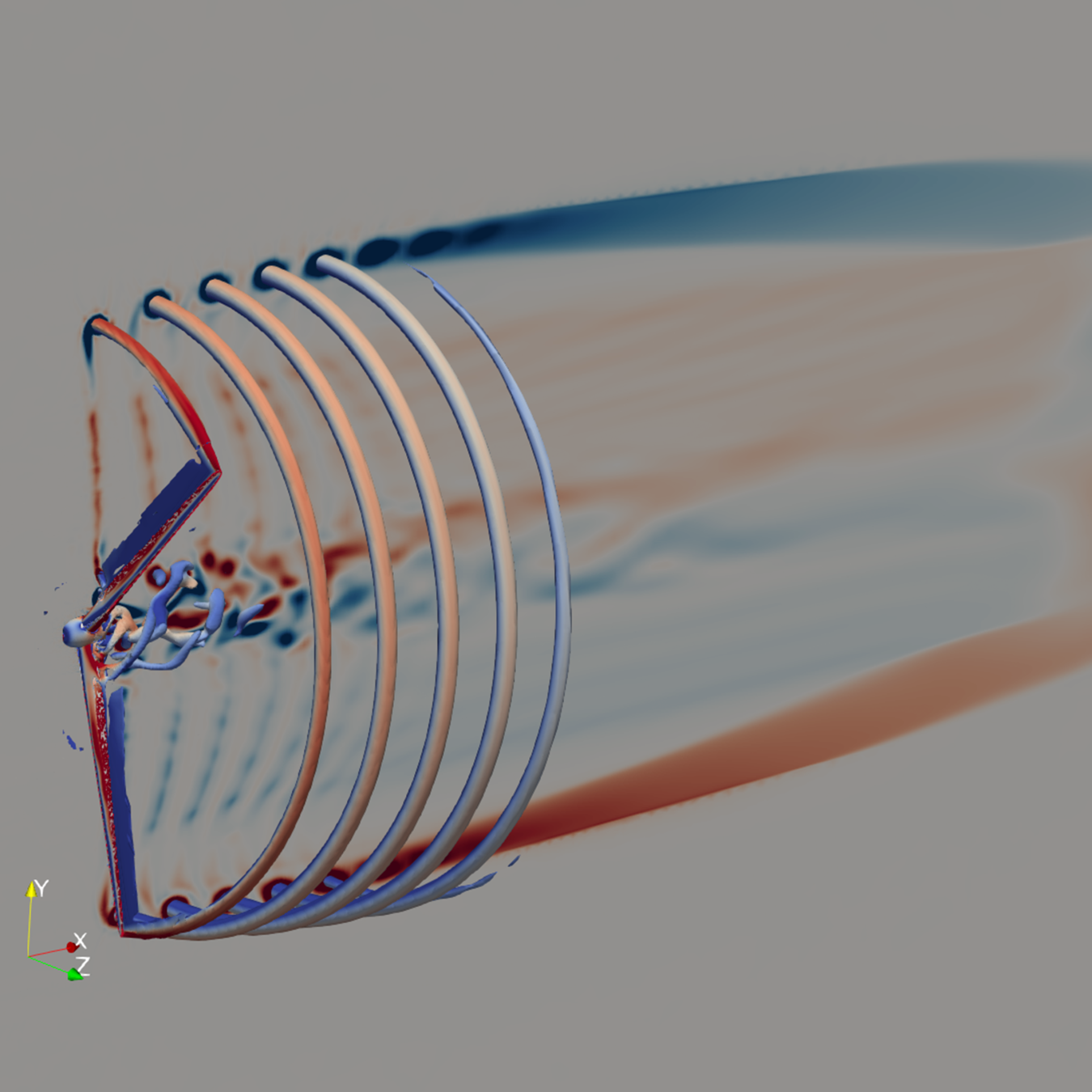
ExaWind is a confidence builder. Until now, predicting the performance of entire wind power plants was a near-impossible task—from anticipating the various movements of turbine blades to understanding how varying wind conditions and blade motion can impact wind power plant operational efficiency.
Designing and installing wind power plants is an expensive and time-consuming venture, and most current modeling and engineering tools are just not up to the task of tackling the intricacies of wind power plant flow dynamics, particularly in offshore environments. Driven by the immense power of high-performance computing (HPC), ExaWind is an open-source suite of physics codes and libraries that enables multifidelity simulation of wind turbines and wind power plants.
Wind Turbines with Large Rotors and Tall Towers Provide Double Dividends
Supersized turbines could reduce costs, enhance value of wind energy—and more

Researchers at DOE's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) analyzed the impact of large wind turbines on grid-system value and illustrated the importance of expanding wind turbine design to focus not only on minimizing direct costs, but also on a broader set of factors that impact the value of wind to the electricity grid. Results demonstrate a possible double dividend—that larger rotors (relative to nameplate capacity) and taller towers might not only reduce levelized cost of energy (LCOE) but also enhance the value of wind energy and provide hidden benefits.
Berkeley Lab’s new research addresses that expanded design need. Results demonstrate a possible double dividend—that larger rotors (relative to nameplate capacity) and taller towers might not only reduce LCOE but also enhance the value of wind energy and provide hidden benefits.
-
 A deeper understanding of bearing axial cracking enables reliability assessments for individual turbines.
A deeper understanding of bearing axial cracking enables reliability assessments for individual turbines. -
 New open-source tool helps stakeholders assess U.S. offshore wind power plant balance-of-system costs.
New open-source tool helps stakeholders assess U.S. offshore wind power plant balance-of-system costs. -
 First-ever simulation could lead to vital understanding of wind power plant performance.
First-ever simulation could lead to vital understanding of wind power plant performance. -
 Testing validates system accuracy, provides comprehensive picture of bird and bat activity.
Testing validates system accuracy, provides comprehensive picture of bird and bat activity. -
 University researchers examine eagle physiology to inform and improve eagle deterrents.
University researchers examine eagle physiology to inform and improve eagle deterrents. -
 First comprehensive study of the U.S. wind fleet shows that the performance of newer plants declines less with age than older plants.
First comprehensive study of the U.S. wind fleet shows that the performance of newer plants declines less with age than older plants. -
 Microgrids, Infrastructure Resilience & Advanced Controls Launchpad project supports distributed wind industry.
Microgrids, Infrastructure Resilience & Advanced Controls Launchpad project supports distributed wind industry. -
New training covers basics and explains how and where systems could be installed.
-
 DOE Labs released data on 2019 U.S. wind installations, technology trends, costs, and more for the offshore, land-based, and distributed wind sectors.
DOE Labs released data on 2019 U.S. wind installations, technology trends, costs, and more for the offshore, land-based, and distributed wind sectors. -
 Applications for CWC 2022 are being accepted now through December 8, 2020.
Applications for CWC 2022 are being accepted now through December 8, 2020. -
 This study highlights the current status of additive manufacturing of magnetic components, such as rotors and stators, for large electrical machines.
This study highlights the current status of additive manufacturing of magnetic components, such as rotors and stators, for large electrical machines. -
 New animation shows how a wind turbine turns wind energy into electricity using the aerodynamic force from the rotor blades.
New animation shows how a wind turbine turns wind energy into electricity using the aerodynamic force from the rotor blades. -
 Brush up on your knowledge of wind! Get the details on a few of the lesser-known wind energy facts.
Brush up on your knowledge of wind! Get the details on a few of the lesser-known wind energy facts. -
 Energy Secretary Brouillette announces the launch of the Advanced Research on Integrated Energy Systems platform at NREL.
Energy Secretary Brouillette announces the launch of the Advanced Research on Integrated Energy Systems platform at NREL. -
 8 new projects aim to drive down cost of distributed wind energy, improve grid support capabilities, and increase turbine certification testing
8 new projects aim to drive down cost of distributed wind energy, improve grid support capabilities, and increase turbine certification testing -
 For the past two decades, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Wind Energy Technologies Office has worked on ways to protect bats at wind farms.
For the past two decades, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Wind Energy Technologies Office has worked on ways to protect bats at wind farms. -
 As we celebrate American Wind Week, let’s look at some of WETO’s most exciting wind energy research this year.
As we celebrate American Wind Week, let’s look at some of WETO’s most exciting wind energy research this year. -
WSU Everett’s unique partnership with Everett Community College prepares team for first-time participation in the Collegiate Wind Competition.
-
 The Roadmap for Wind Cybersecurity outlines the increasing challenges of cyber threats to the wind industry.
The Roadmap for Wind Cybersecurity outlines the increasing challenges of cyber threats to the wind industry. -
 Jane Sandoval enters her master's program this fall with years of energy experience, including her work in DOE's 2020 Collegiate Wind Competition.
Jane Sandoval enters her master's program this fall with years of energy experience, including her work in DOE's 2020 Collegiate Wind Competition. -
 Beyond Power, Wind Plants Can Provide a Full Suite of Essential Reliability Services to the Grid
Beyond Power, Wind Plants Can Provide a Full Suite of Essential Reliability Services to the Grid -
 After four days of intense virtual presentations, the Energy Department announced the winners of the 2020 Collegiate Wind Competition.
After four days of intense virtual presentations, the Energy Department announced the winners of the 2020 Collegiate Wind Competition.
-
 Applications are due October 19, 2020, for Round 3: Electrical Systems and Innovation; Technologies To Mitigate Use Conflicts.
Applications are due October 19, 2020, for Round 3: Electrical Systems and Innovation; Technologies To Mitigate Use Conflicts. -
 Two wind energy projects selected among 49 new Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer projects across 23 states.
Two wind energy projects selected among 49 new Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer projects across 23 states. -
DOE announced selections of more than $33 million in funding for 82 projects supported by the Technology Commercialization Fund.
-
 National Offshore Wind R&D Consortium announces 12 new research projects, representing an investment of $17.3 million.
National Offshore Wind R&D Consortium announces 12 new research projects, representing an investment of $17.3 million.
Featured Publications
The following is a curated listing of recent or high-profile publications from WETO and DOE National Laboratories. Visit the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy’s Wind Technology Resource Center for research reports, publications, data sets, and online tools developed by National Laboratories and their facilities.
- A Gravo-Aeroelastically Scaled Wind Turbine Rotor at Field-Prototype Scale with Strict Structural Requirements
- Aeroacoustics Noise Model of OpenFAST
- American WAKE experimeNt (AWAKEN)
- An LES-Based Airborne Doppler Lidar Simulator and its Application to Wind Profiling in Inhomogeneous Flow Conditions
- Atmosphere to Electrons Data Archive and Portal (fact sheet)
- Assessing the Blockage Effect of Wind Turbines and Wind Farms Using an Analytical Vortex Model
- Assessment of Low-Altitude Atmospheric Turbulence Models for Aircraft Aeroelasticity
- The Curled Wake Model: Equivalence of Shed Vorticity Models
- Design and Analysis of a Spatially Heterogeneous Wake (preprint)
- Development of a Time–Height Profile Assimilation Technique for Large-Eddy Simulation
- Multimodel Validation of Single Wakes in Neutral and Stratified Atmospheric Conditions
- Multi-Scale Simulation of Wind Farm Performance during a Frontal Passage (animation)
- Preliminary Introduction of a Free Vortex Wake Method into OpenFAST
- Simulating Real Atmospheric Boundary Layers at Gray-Zone Resolutions: How Do Currently Available Turbulence Parameterizations Perform?
- Wake Statistics of Different-Scale Wind Turbines under Turbulent Boundary Layer Inflow
- Wind Energy High-Fidelity Model Verification and Validation Roadmap
- Wind Farm Layout Optimization with Loads Considerations
- An Overview of Wind Energy Production Prediction Bias, Losses, and Uncertainties
- Land-Based Wind Energy Cost Trends in Germany, Denmark, Ireland, Norway, Sweden and the United States
- The Hidden Value of Large-Rotor, Tall-Tower Wind Turbines in the United States
- Opportunities for and Challenges to Further Reductions in the “Specific Power” Rating of Wind Turbines Installed in the United States
- Wind Energy Technology Data Update: 2020 Edition
- Computational Analysis of Deployable Wind Turbine Systems in Defense Operational Energy Applications
- Defense & Disaster Deployable Turbine (fact sheet)
- Distributed Wind Competitiveness Improvement Project (fact sheet)
- Distributed Wind Tools Assessing Performance (fact sheet)
- Microgrids, Infrastructure Resilience, and Advanced Controls Launchpad (fact sheet)
- 2019 Distributed Wind Data Summary
- Ultrasonic Acoustic Deterrents Significantly Reduce Bat Fatalities at Wind Turbines
- Auditory Performance in Bald Eagles and Red-Tailed Hawks: A Comparative Study of Hearing in Diurnal Raptors
- Thermaltracker-3D: A Thermal Stereo Vision System for Quantifying Bird and Bat Activity at Offshore Wind Energy Sites
- WREN: Working Together To Resolve Environmental Effects of Wind Energy (fact sheet)
- Opportunities for Research and Development of Hybrid Power Plants
- Avangrid Renewables Tule Wind Farm Demonstration of Capability to Provide Essential Grid Services
- Motivation and Options for Deploying Hybrid Generator-Plus-Battery Projects Within the Bulk Power System
- The Potential Impact of Offshore Wind Energy on a Future Power System in the U.S. Northeast
- Wind Cybersecurity Roadmap
- A Cross-Sectional Aeroelastic Analysis and Structural Optimization Tool for Slender Composite Structures
- Additive Manufacturing of Soft Magnets for Electrical Machines -- A Review
- On the Scaling of Wind Turbine Rotors (preprint)
- Supersized Wind Turbine Blade Study: R&D Pathways for Supersized Wind Turbine Blades
- A Methodology for Reliability Assessment and Prognosis of Bearing Axial Cracking in Wind Turbine Gearboxes
- Advanced Wind Turbine Drivetrain Topology for Improving System Reliability: Cooperative Research and Development Final Report, CRADA Number CRD-10-400
- Report of the Condition of a General Electric Transportation Systems Gearbox
- The Effect of Lubricant Composition on White Etching Crack Failures
- The Influence of Steel Microstructure and Inclusion Characteristics on the Formation of Premature Bearing Failures with Microstructural Alterations
- Validation of Combined Analytical Methods to Predict Slip in Cylindrical Roller Bearings
- A Systems Engineering Vision for Floating Offshore Wind Cost Optimization
- Comparing Offshore Wind Energy Procurement and Project Revenue Sources Across U.S. States
- Definition of the UMaine VolturnUS-S Reference Platform Developed for the IEA Wind 15-Megawatt Offshore Reference Wind Turbine
- Evaluation of Different Wind Fields for the Investigation of the Dynamic Response of Offshore Wind Turbines
- Implementation of Substructure Flexibility and Member-Level Load Capabilities for Floating Offshore Wind Turbines in OpenFAST
- Large Eddy Simulations of Offshore Wind Turbine Wakes for Two Floating Platform Types
- Offshore Wind Electrical Safety Standards Harmonization: Workshop Proceedings
- ORBIT: Offshore Renewables Balance-of-System and Installation Tool
- Validation of Numerical Models of the Offshore Wind Turbine From the Alpha Ventus Wind Farm Against Full-Scale Measurements Within OC5 Phase III
- Cost of Floating Offshore Wind Energy Using New England Aqua Ventus Concrete Semisubmersible Technology
- IEA Wind TCP Task 37: Definition of the IEA 15-Megawatt Offshore Reference Wind Turbine
- National Offshore Wind Research and Development Consortium: Research and Development Roadmap
- The Vineyard Wind Power Purchase Agreement: Insights for Estimating Costs of U.S. Offshore Wind Projects
- 2019 Offshore Wind Technology Data Update
- 2018 Offshore Wind Technologies Market Report
- Can Machine Learning Improve the Model Representation of TKE Dissipation Rate in the Boundary Layer for Complex Terrain? (preprint)
- Characterizing Thunderstorm Gust Fronts Near Complex Terrain
- Enhancement of Unsteady and 3D Aerodynamics Models Using Machine Learning
- Evaluating the WFIP2 Updates to the HRRR Model using Scanning Doppler Lidar Measurements in the Complex Terrain of the Columbia River Basin
- ExaWind: A Multifidelity Modeling and Simulation Environment for Wind Energy
- Lidar Buoy Loan Program (fact sheet)
- Workshop on Research Needs for Offshore Wind Resource Characterization
- Xcompact3D: An Open-Source Framework for Solving Turbulence Problems on a Cartesian Mesh
Subscribe to learn more about DOE Wind Energy Technologies Office R&D projects, news, accomplishments, and recent publications.

