-- This project is inactive --
Boston University and its partners, under the 2012 SunShot Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) R&D FOA, are working to develop a new method to keep solar collectors dirt- and dust-free and thereby maintain high optical efficiency.
Approach
This project aims to develop large-scale prototypes, cost-effective manufacturing processes, and commercialization of the technology in large-scale CSP devices for their applications in semi-arid and desert climates. Specific objectives include:
- Establishing proof-of-concept of the application of the electrodynamic screen (EDS) for self-cleaning solar concentrators
- Producing and evaluating laboratory-scale prototypes of self-cleaning solar collectors, including flat mirrors and curved mirrors
- Testing the EDS-incorporated collectors for their optical efficiency of sunlight, dust-removal efficiency, power requirements, and durability.
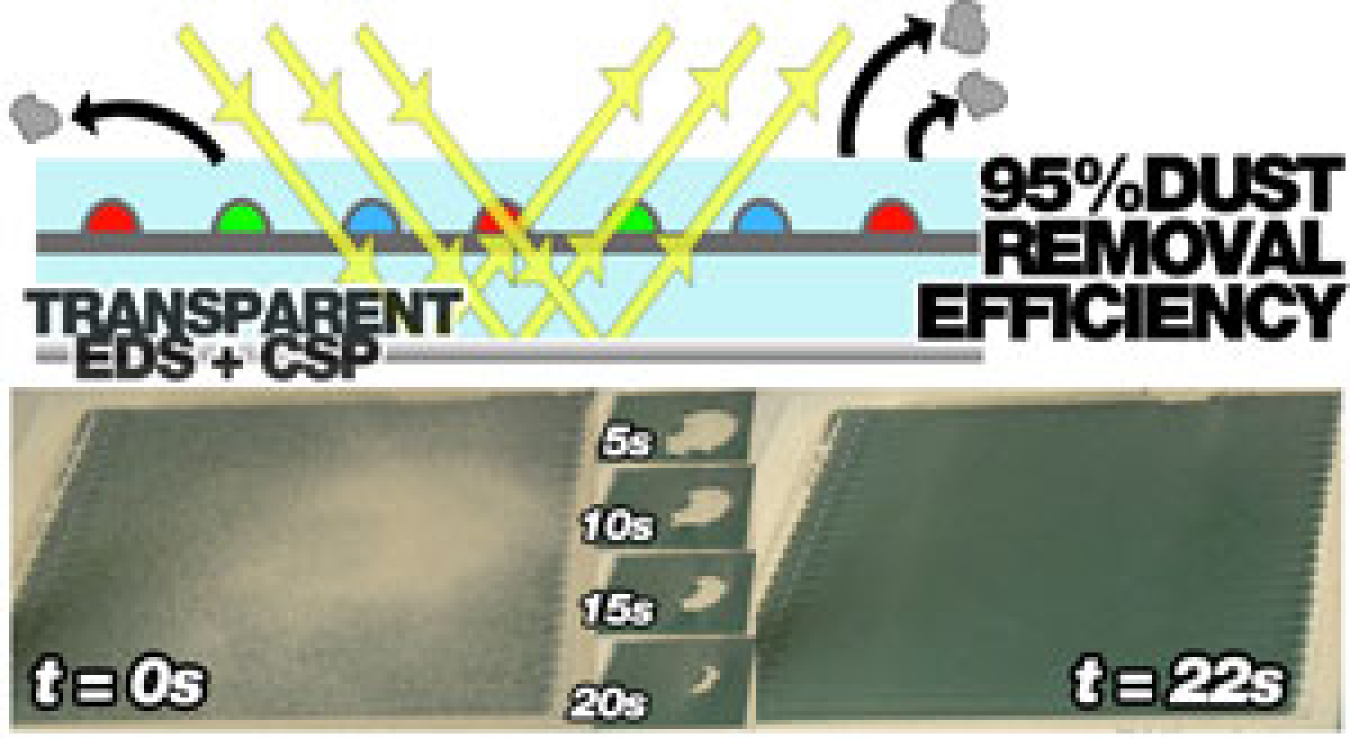
This graphic illustrates the project's self-cleaning concentrated solar power collectors.
Innovation
This novel EDS-based system may be the only one in the world that:
- Can remove dust with more than 90% efficiency in a matter of minutes
- Uses a very small fraction of energy produced by the solar collectors
- Minimizes the use of water and maintenance costs.
If successful, these valuable features will give the system high potential to be widely deployed.
Publications, Patents, and Awards
The CSP R&D program seeks to accelerate progress toward the cost target of $0.06 per kilowatt-hour through novel and revolutionary research into CSP technologies. Learn about other concentrating solar power research.

