Highlights
-

- Wind
Learn how wind turbines operate to produce power from the wind.November 23, 2024 -
-
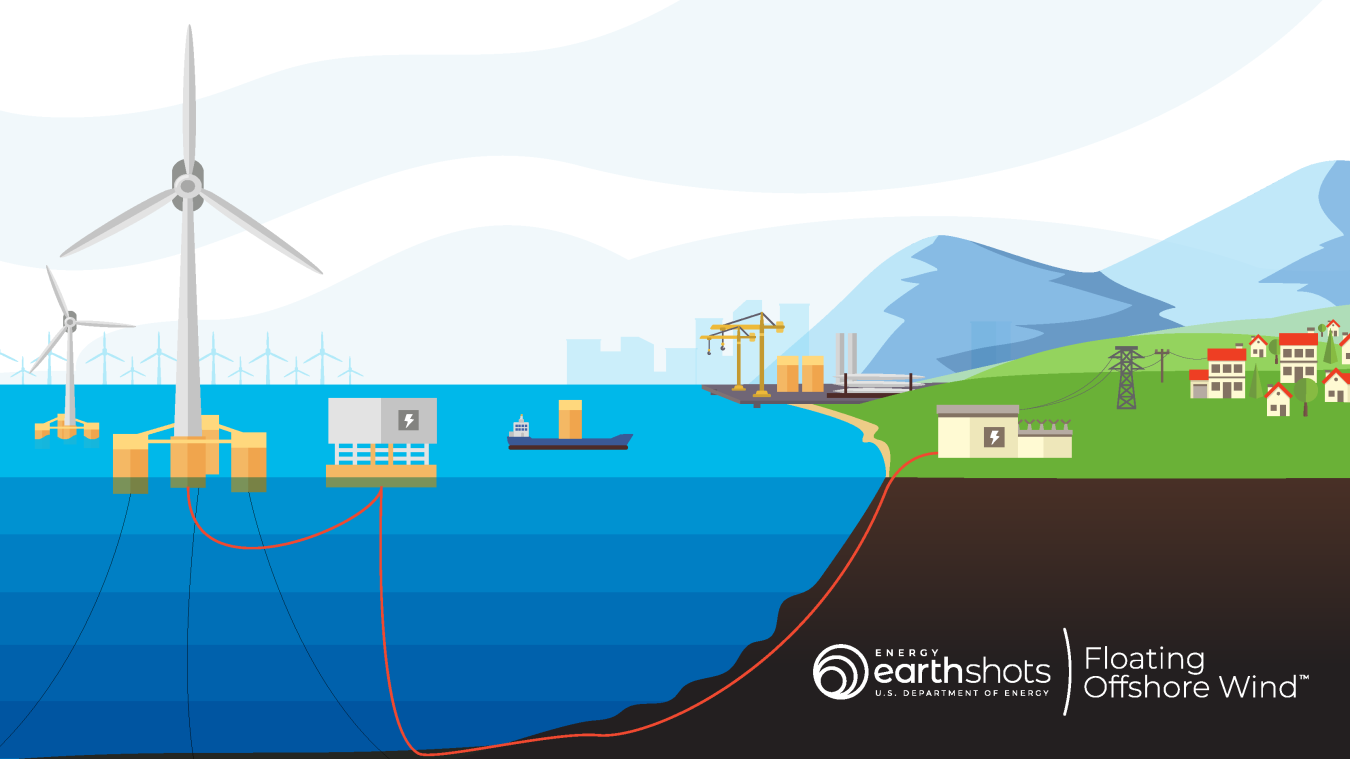 An initiative to drive U.S. leadership in floating offshore wind design, development, and manufacturing.November 23, 2024
An initiative to drive U.S. leadership in floating offshore wind design, development, and manufacturing.November 23, 2024
Advancing a Domestic Clean Energy Future through Wind Energy
Why Wind Energy?
Wind energy is a cornerstone of the nation’s power system, offering cost-competitive, emission-free, and locally produced electricity across the country. Wind energy presents a unique opportunity to harness energy in areas where our country's populations need it most. This includes offshore wind’s potential to provide power to population centers near coastlines, and land-based wind's ability to deliver electricity to rural communities and islands with few other local sources of power.
Leveraging the nation's abundant wind resources for electric power generation helps the nation increase its competitiveness, diversify its energy supply, increase energy security and independence, reduce emissions of air pollutants, save water that would otherwise be used by thermal power generation, and provide affordable electricity across the country. In addition, wind energy deployment helps stimulate the revitalization of key sectors of the economy by investing in infrastructure and creating long-term skilled jobs.
Wind power creates jobs and bolsters the U.S. economy. Nearly 150,000 people are working in the U.S. wind industry across all 50 states, and that number continues to grow. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, wind turbine service technicians represent one of the fastest growing U.S. jobs of the decade.
Wind power benefits local communities. Wind projects deliver an estimated $2 billion in state and local tax payments and land-lease payments each year. Communities that develop wind energy can use the extra revenue to put towards school budgets, reduce the tax burden on homeowners, and address local infrastructure projects.
Wind power is a clean and renewable energy source. Wind energy is a form of clean energy, meaning it doesn't emit pollution, resulting in less pollution going into the air, oceans, and environment that can cause health problems or harm the environment.
What Are the Main Types of Wind Energy?
Offshore Wind Energy
Offshore wind turbines in water depths less than 60 meters can be fixed directly to the bottom of the ocean, known as fixed-bottom offshore wind turbines. About two-thirds of U.S. offshore wind energy potential exists over waters too deep for today’s fixed-bottom wind turbine foundations and instead require floating offshore wind platforms. Electricity from offshore wind is brought to shore via high-voltage direct current transmission lines, then connected to the grid to power homes and businesses.
Land-Based Wind Energy
Land-based, utility-scale wind energy projects use highly efficient, state-of-the-art wind turbines that generate cost-competitive electricity at power-plant scales. They can be owned and run by a utility company that then sells the power the plant makes to users, like homeowners, who connect to the electrical grid.
Distributed Wind Energy
Distributed wind energy describes wind energy projects that serve local energy demand generating on-site electricity for homes, schools, businesses, and farms. Wind turbines used as a distributed energy resource can be connected at the distribution level of an electricity delivery system (or in off-grid applications) to serve on-site energy demand, or support operation of local electricity distribution networks.
DOE's Role in Advancing U.S. Wind Energy
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has been a global leader in supporting critical wind energy research and development (R&D) for decades, helping usher in commercial wind energy production. These investments have contributed to the rise of today’s wind energy sector.
DOE's Wind Energy Technologies Office (WETO) funds wind energy R&D activities that
- Innovate technologies needed to advance land-based, offshore, and distributed wind systems
- Reduce the cost of wind energy and minimize environmental impacts
- Demonstrate technological solutions for greater siting flexibility, lowered costs, and optimized performance
- Generate world-class insights and data in wind engineering, environmental and social sciences, and grid integration.
Other DOE offices that support wind energy include:
- The Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) — Funding high potential, high-impact technologies
- Grid Deployment Office — Offshore wind transmission federal planning and support
- Office of Electricity — Grid-enhancing technologies for reliability and energy storage
- Loan Programs Office — Financing renewable energy projects
- Office of Clean Energy Demonstrations — Funding clean energy demonstration projects
- Federal Energy Management Program — Funding and facilitating Federal clean energy projects.
Advancing U.S. wind energy requires regular collaboration with government agencies, academic institutions, small businesses, nonprofits, environmental groups, states, Tribal nations, communities, the international research community, and other industry stakeholders to identify and address challenges that face the wind energy sector.
DOE encourages researchers across disciplines to apply for funding to support innovative projects that advance the wind energy sector. Learn more about DOE funding opportunities for wind energy research and development, as well as tax credits and incentives for wind energy deployment.
Wind Energy 101
What Is Wind Energy?
Visit our basics pages to learn how wind energy produces power and see an animation of how wind turbines work.

Collegiate Wind Competition
DOE’s Collegiate Wind Competition helps college students prepare for jobs in the wind and renewable energy workforce through real-world experiences with wind energy technology, project development, finance, communications, and outreach. By participating in the competition, schools and students connect with wind energy experts and industry contacts, enhancing schools' curriculum offerings and strengthening students' professional networks.
Wind Energy Technologies Office R&D Projects Map
WETO leads the nation's efforts to research and develop innovative technologies, lower the costs, and enable and accelerate the deployment of wind energy throughout the nation. The office has a comprehensive portfolio and invests through cooperative agreements with a variety of businesses, universities, laboratories, and other organizations.
Learn more about the Office's R&D portfolio through the interactive map below. Users can apply the filters on the left or click on a specific state. The projects that meet your chosen criteria will populate in a table below the map. Further refinement can be made by adjusting the filters or using the search box to control the information displayed, or zoom in to see projects in any specific region or state.
Resources
-
 Wind Energy Technologies Office fact sheets, reports, and other information resources.January 17, 2025
Wind Energy Technologies Office fact sheets, reports, and other information resources.January 17, 2025 -
Press Releases
Upcoming Events
-
Mar 3Operations, Maintenance & Safety ConferenceMar 3 - Mar 5 Starts 9am CST View Event Details for Operations, Maintenance & Safety Conference
-
Apr 14Siting and Permitting ConferenceApr 14 - Apr 16 Starts 12pm MDT View Event Details for Siting and Permitting Conference
-
Apr 28International Partnering ForumApr 28 - May 1 Starts 7am EDT View Event Details for International Partnering Forum
-
May 5Offshore Technology ConferenceMay 5 - May 8 Starts 8am CDT View Event Details for Offshore Technology Conference


