Jay TIlden recently toured the Leonardo Helicopter assembly plant in Philadelphia to see the new aircraft NNSA has ordered.
National Nuclear Security Administration
September 6, 2023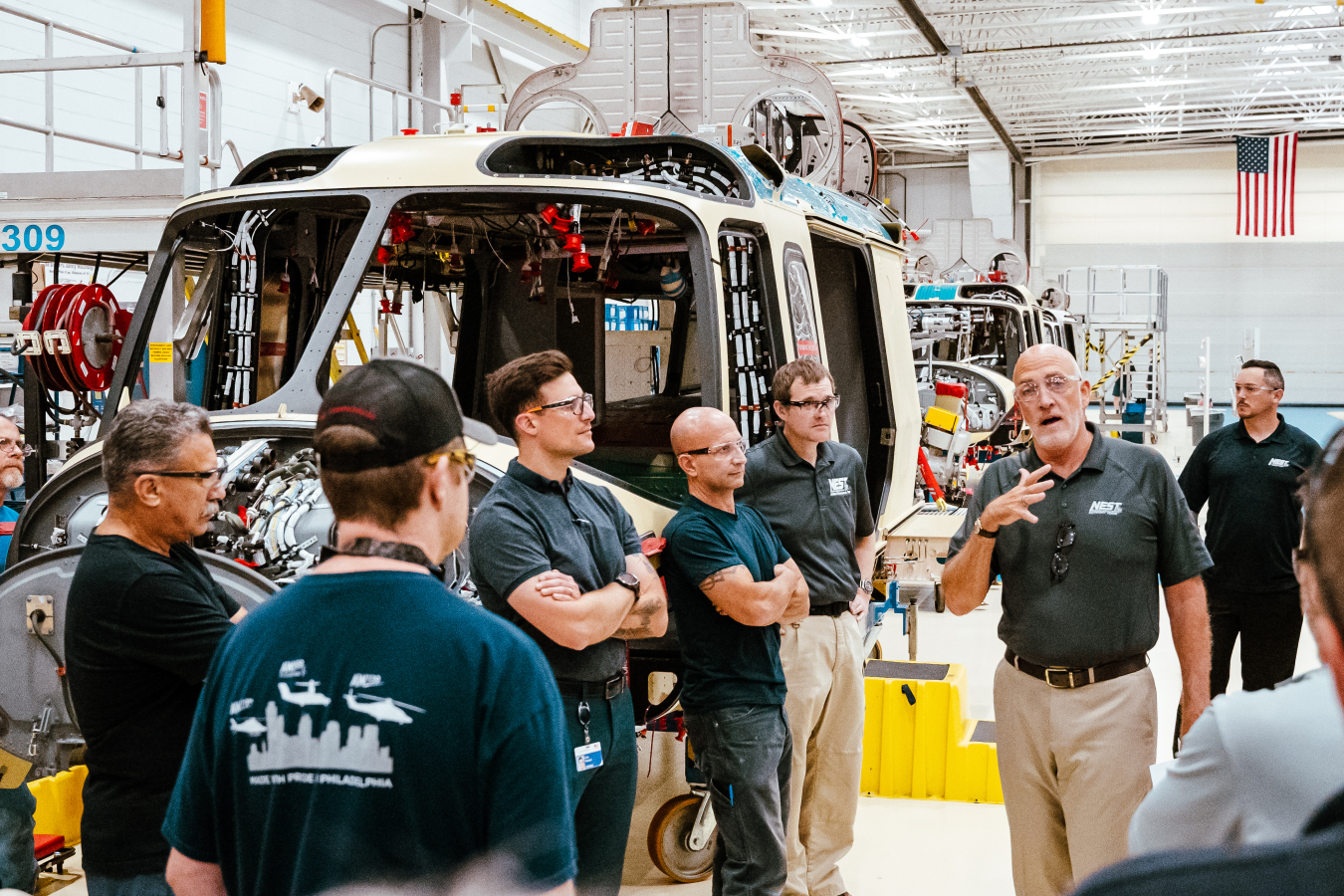
Little known fact: NNSA has its very own air force. Specifically, a fleet of fixed-wing and rotary-wing (helicopter) aircraft that comprise the Aerial Measuring System (AMS).

Part of the Nuclear Emergency Support Team (NEST), AMS aircraft are used for a wide range of national security and public safety missions. Equipped with specialized radiation detection equipment, AMS protects large public gatherings – such as the Super Bowl, the Indy 500, and presidential inaugurations – from nuclear and radiological threats and responds to radiation releases in the environment.
“The helicopters being produced today are a final step in our journey that started in 2016 to recapitalize our stateside civil preparedness capability known as the Aerial Measuring System,” said Jay Tilden, NNSA’s Associate Administrator for Counterterrorism and Counterproliferation.
The current AMS helicopters – one based at Nellis Air Force Base in Nevada and the other at Joint Base Andrews in Maryland – are almost 30 years old and have exceeded their service lives. As part of a program to recapitalize the entire AMS fleet, NEST received funding in 2020 to procure two new AgustaWestland139 (AW139) helicopters, which are expected to be delivered in early 2024. (An earlier phase of the AMS aircraft recapitalization program occurred in 2019, when NEST took delivery of three new King Air 350ER fixed-wing aircraft.)
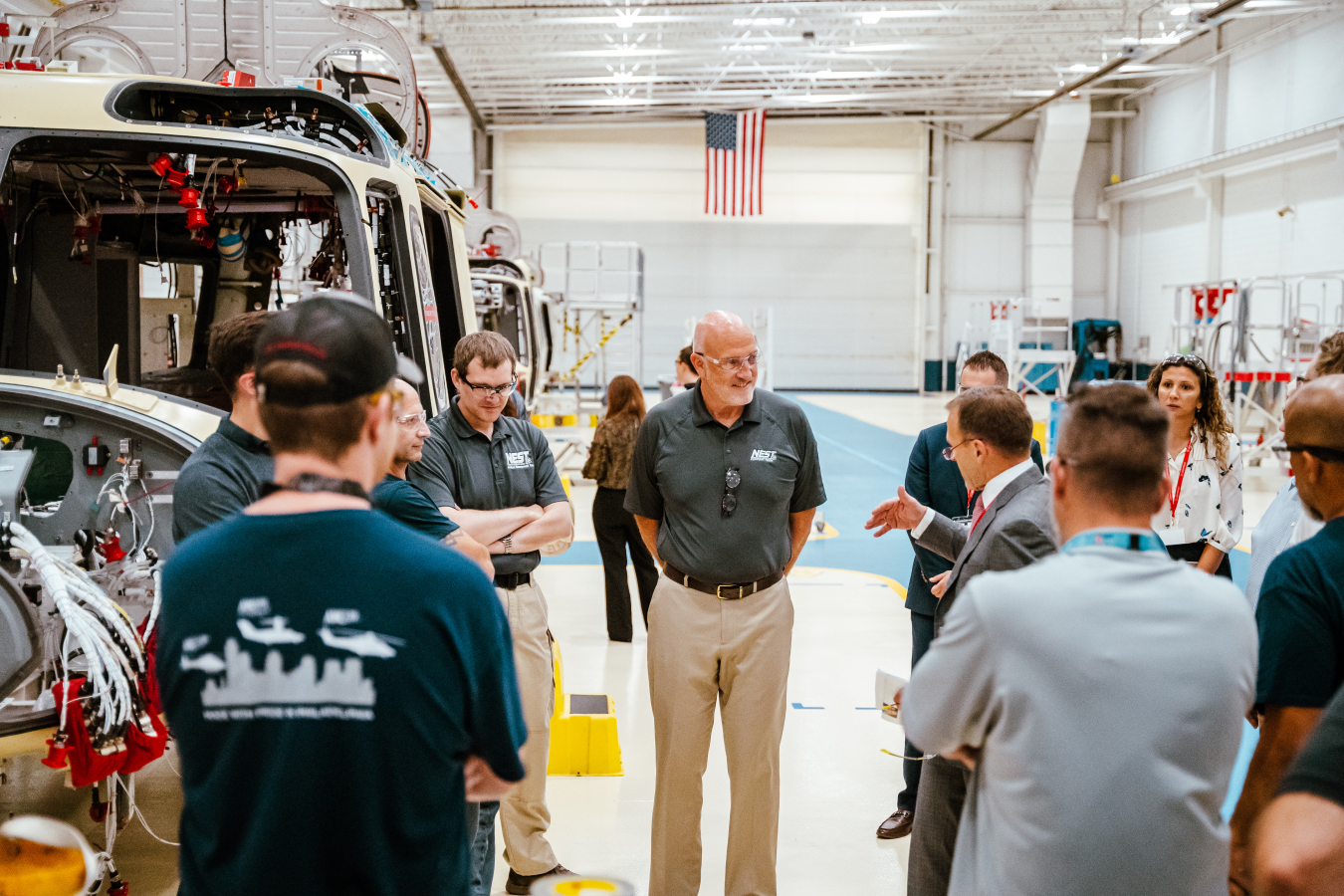

The new AMS helicopters are currently being manufactured at the Leonardo Helicopter assembly plant in Philadelphia. Tilden, who has spearheaded the aircraft recapitalization program, recently toured the facility to observe the manufacturing process as the two helicopters move through the final stages of assembly. Accompanied by other senior NEST leaders, Tilden thanked the Leonardo workforce for their contribution to a critical nuclear security mission.
“NEST has a proud heritage of preventing fearful events and providing decisionmakers with dispassionate scientific advice during fearful events, and these aircraft are a critical element of that mission,” Tilden said. “AMS scientists, technical personnel, and pilots are on-call 24 hours per day / 365 days per year to respond to nuclear incidents and accidents. It’s vital that these aircraft be as reliable and versatile as the men and women who operate them for the American people.”
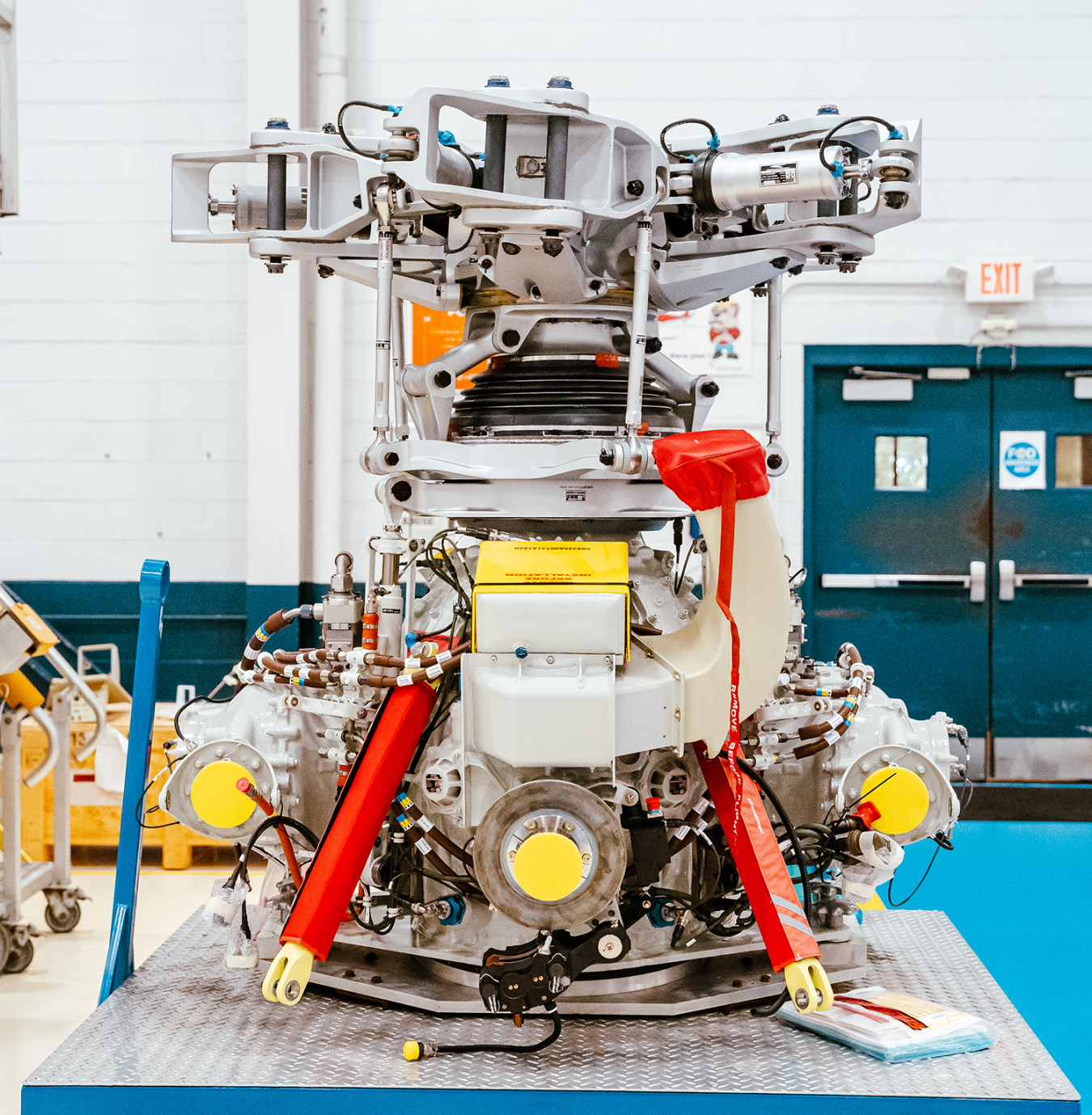
The transition from legacy helicopters to modern, state-of-the-art platforms will benefit the AMS program well into the future. Response times will improve along with an increased capacity to deploy additional sensors for enhanced data collection, resulting in more timely and beneficial technical guidance. In addition, this greater capability provides an increased margin of safety to the public and the environment.
Modern helicopters will bring NEST’s aerial capability in line with other incident responders such as the Federal Bureau of Investigation, Department of Homeland Security, and state and local police, fire, emergency medical services.
Why the AW139?
- A solicitation for two helicopters incorporating a list of 105 requirements necessary for aircraft to meet NEST mission requirements was issued in February 2019. That free and open competition determined that the AW139 proposal met the requirements and offered best value to the U.S. government.
- The AW139 is a modern twin-engine helicopter designed as a versatile and multi-role aircraft. Since its certification in 2005, Leonardo has delivered more than 1,050, and the fleet has amassed more than 2.5 million flight hours since.
- The AW139 has modern flight decks with flight operations quality assurance capabilities, modern auto pilots with fourth axis capabilities, component usage and monitoring systems, and state-of-the-art maintenance programs.
The helicopters being produced today are a final step in our journey that started in 2016 to recapitalize our stateside civil preparedness capability known as the Aerial Measuring System.
Benefits of the new helicopters
- The cruise speed of the new helicopters is 190 mph, with enough fuel to fly almost 3.5 hours or more than 650 miles between fill-ups – that’s more than 1.5 hours and 400 miles further than the existing helicopters can travel.
- The flight time of the AW139 greatly improves the efficiency of an aerial survey and decreases the time needed to provide survey results to incident managers.
- The AW139 can carry 1,800 pounds of additional payload than the current helicopters. This allows additional radiation detectors to be carried on board for improved survey results and greater resolution.
- The new helicopter includes state-of-the-art integrated avionics and fully digital glass cockpit to minimize pilot workload and improve situational awareness. Communications equipment will enable the pilots and crew to communicate with operations on the ground such as NEST’s Radiological Assistance Program and police, fire, and emergency services. A satellite communication system provides both data and voice capability to ensure real-time measurements are transmitted back to DOE’s national laboratories for interpretation and faster product delivery to an incident commander.
- The AW139 uses digital electronic systems, which allow for modular upgrades in the future. This feature enables seamless system upgrades or capability enhancements such as forward looking infrared or other thermal imaging cameras, or video and still images to enhance aerial survey interpretation products.

