PROJECT SUMMARY
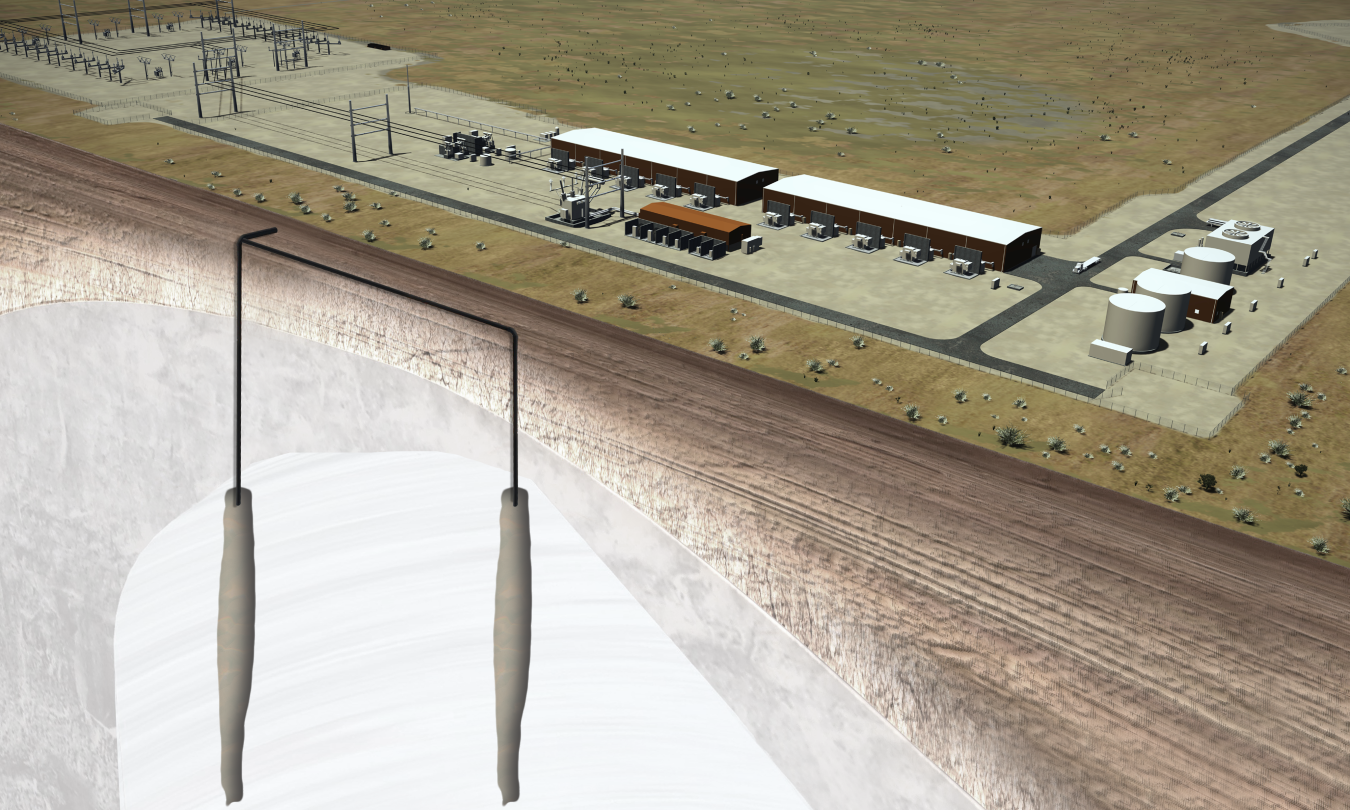
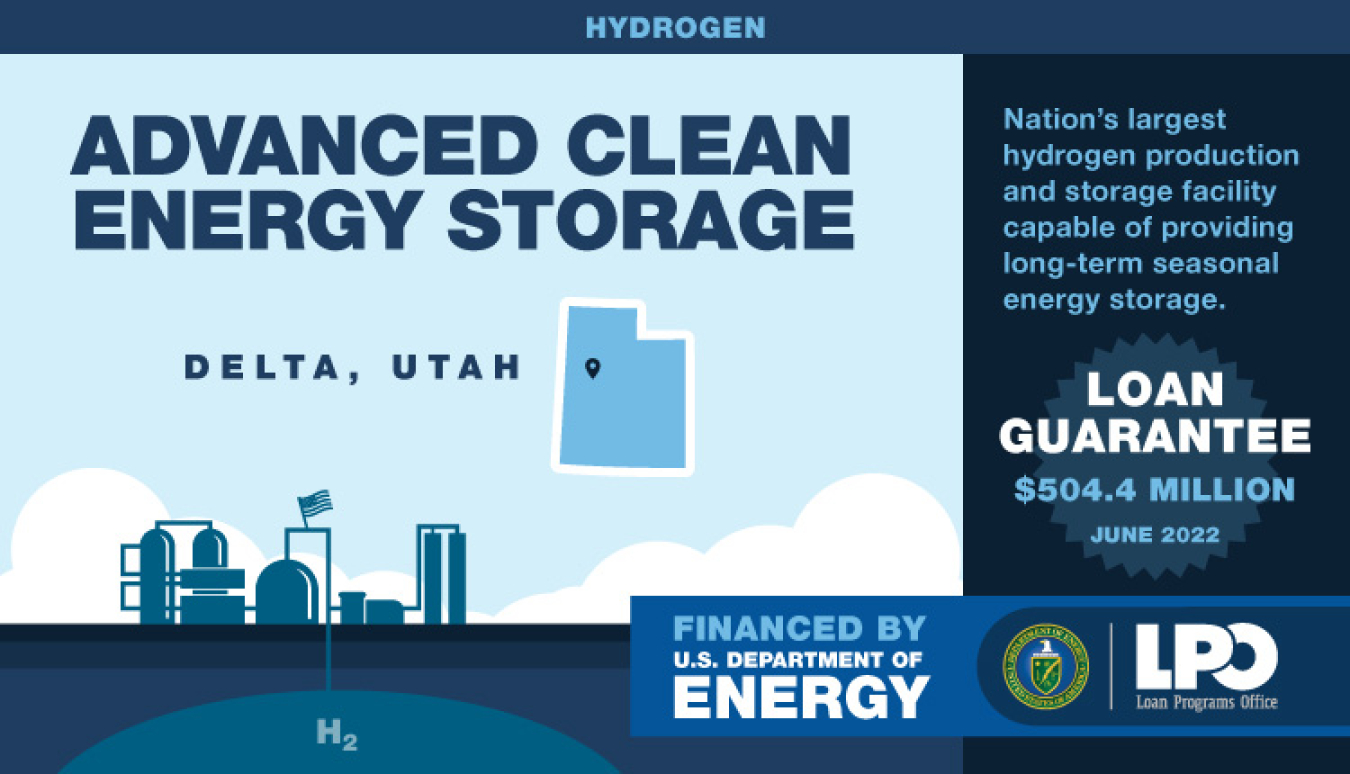
In June 2022, the Department of Energy issued a $504.4 million loan guarantee to finance Advanced Clean Energy Storage, a clean hydrogen and energy storage facility capable of providing long-term, seasonal energy storage. The facility in Delta, Utah, will combine 220 megawatts of alkaline electrolysis with two massive 4.5 million barrel salt caverns to store clean hydrogen. Advanced Clean Energy Storage will capture excess renewable energy when it is most abundant, store it as hydrogen, then deploy it as fuel for the Intermountain Power Agency’s (IPA) IPP Renewed Project—a hydrogen-capable gas turbine combined cycle power plant that intends to incrementally be fueled by 100 percent clean hydrogen by 2045.
TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION
Advanced Clean Energy Storage uses a 220-megawatt bank of electrolyzers and intermittent renewable energy to produce hydrogen, store it in salt caverns, and deliver that hydrogen for future dispatchable generation. The scale of deployed electrolyzers as well as the use of salt caverns to store hydrogen are both significant innovations.
ECONOMIC IMPACT
Advanced Clean Energy Storage is expected to create up to 400 construction jobs and 25 operations jobs.
CLIMATE BENEFIT
Advanced Clean Energy Storage may contribute to grid stabilization and reduction of curtailment of renewable energy by using hydrogen to provide long-term storage. The stored hydrogen is expected to be used as fuel for a hybrid 840 MW combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) power plant that will be built to replace a retiring 1,800 MW coal-fired power plant. The project is estimated to help prevent 126,517 metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually based on the difference in the emission profiles of the IPP turbines between 100 percent natural gas fuel to a 70 percent natural gas and 30 percent hydrogen fuel blend.
| PROJECT SUMMARY | Owners | Mitsubishi Power Americas, Inc., Magnum Development, Haddington Ventures |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Delta, UT | |
| FINANCIAL SUMMARY | Loan Program | Title 17 |
| Loan Type | Loan Guarantee | |
| Loan Amount1 | $504.4 Million | |
| Issuance Date | June 2022 | |
| ENERGY SUMMARY | Operation Status | Under Development |
| Electrolyzer Capacity | 220 MW | |
| ECONOMIC IMPACT2 | Permanent U.S. Jobs Supported | 25 |
| U.S. Construction Jobs Supported | 400 | |
| CO2 Emissions Prevented Annually3 | 126,517 Metric Tons | |
| NOTES |
1 All information up-to-date as of June 2022 2 Estimated at the time of closing. 3 The GHG reduction for the Project is based on the difference in the emission profiles of the IPP turbines between 100 percent natural gas fuel to a 70 percent natural gas and 30 percent hydrogen fuel blend. |
PROJECT PHOTOS


