The National Renewable Energy Laboratory has recently upgraded their Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Projection (EVI-Pro) Lite tool.
November 23, 2020The National Renewable Energy Laboratory has recently upgraded their Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Projection (EVI-Pro) Lite tool to inform industry stakeholders about the electricity needed to charge plug-in vehicles. Within the tool, users can customize to their own specifications for:
- Location (city and state)
- Number of plug-in vehicles
- Average daily miles per vehicle
- Average ambient temperature
- All-electric vehicle share
- Vehicle type
- Share of workplace/home charging
- Charging levels
- Charging time of day.
Real-world travel data from consumers are used to model future requirements for residential, workplace, and public charging under different scenarios. The model results for the electric load profile for a fleet of 1,000 plug-in vehicles in Indianapolis, IN, are shown below as an example. EVI-Pro Lite is also useful for estimating the number of electric vehicle chargers needed in an area to sustain a certain number of plug-in vehicles.
Example of EVI-Pro Lite Results
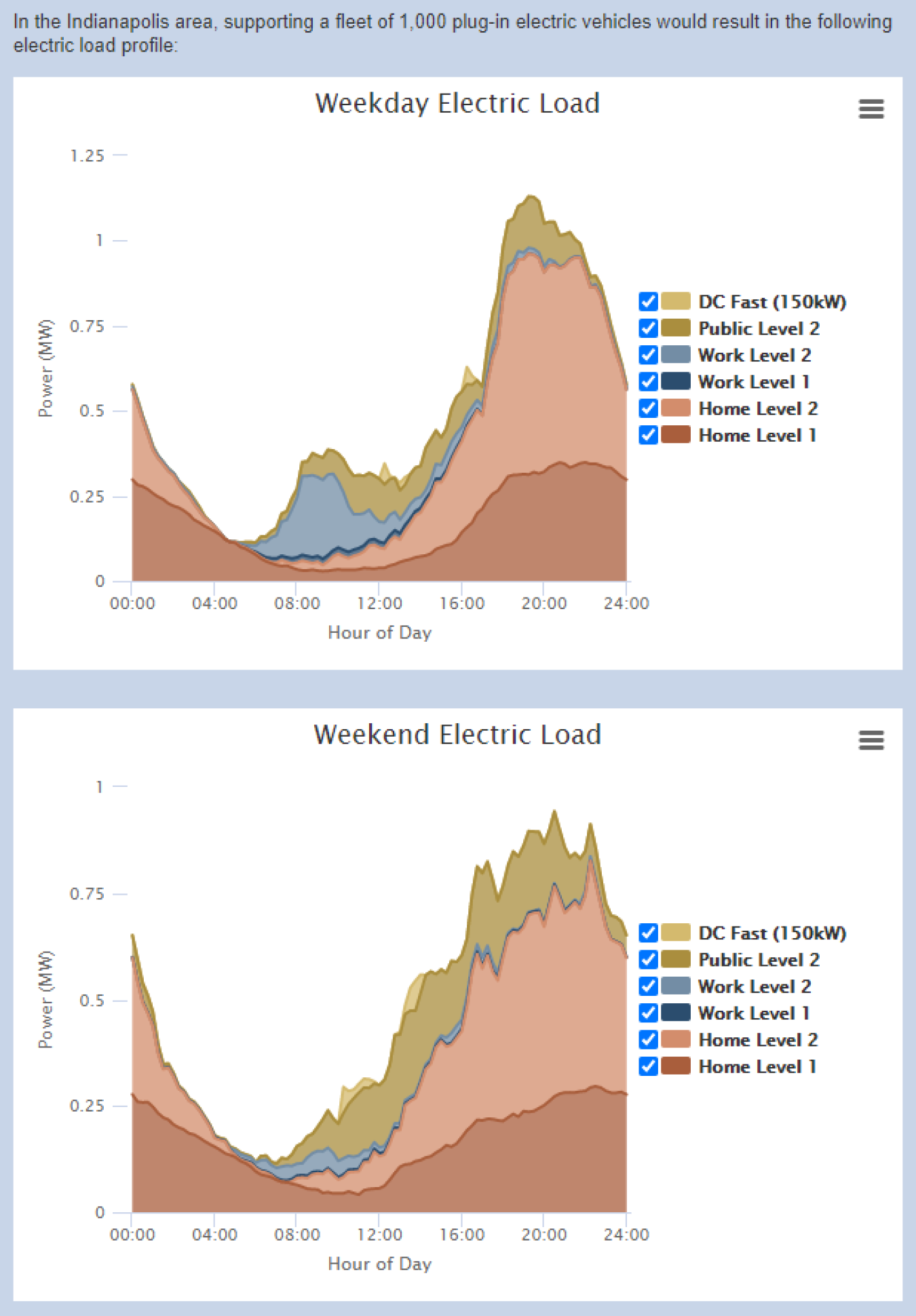
Note: EVI-Pro Lite has been developed through a collaboration between the National Renewable Energy Laboratory and the California Energy Commission, with additional support from the U.S. Department of Energy's Vehicle Technologies Office. Load profile analysis capabilities in EVI-Pro Lite have been developed through a collaborative effort between the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and Schatz Energy Research Center at Humboldt State University.
Source: Alternative Fuels Data Center, Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Projection (EVI-Pro) Lite.

