Lead Performer: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory – Berkeley, CA
April 25, 2017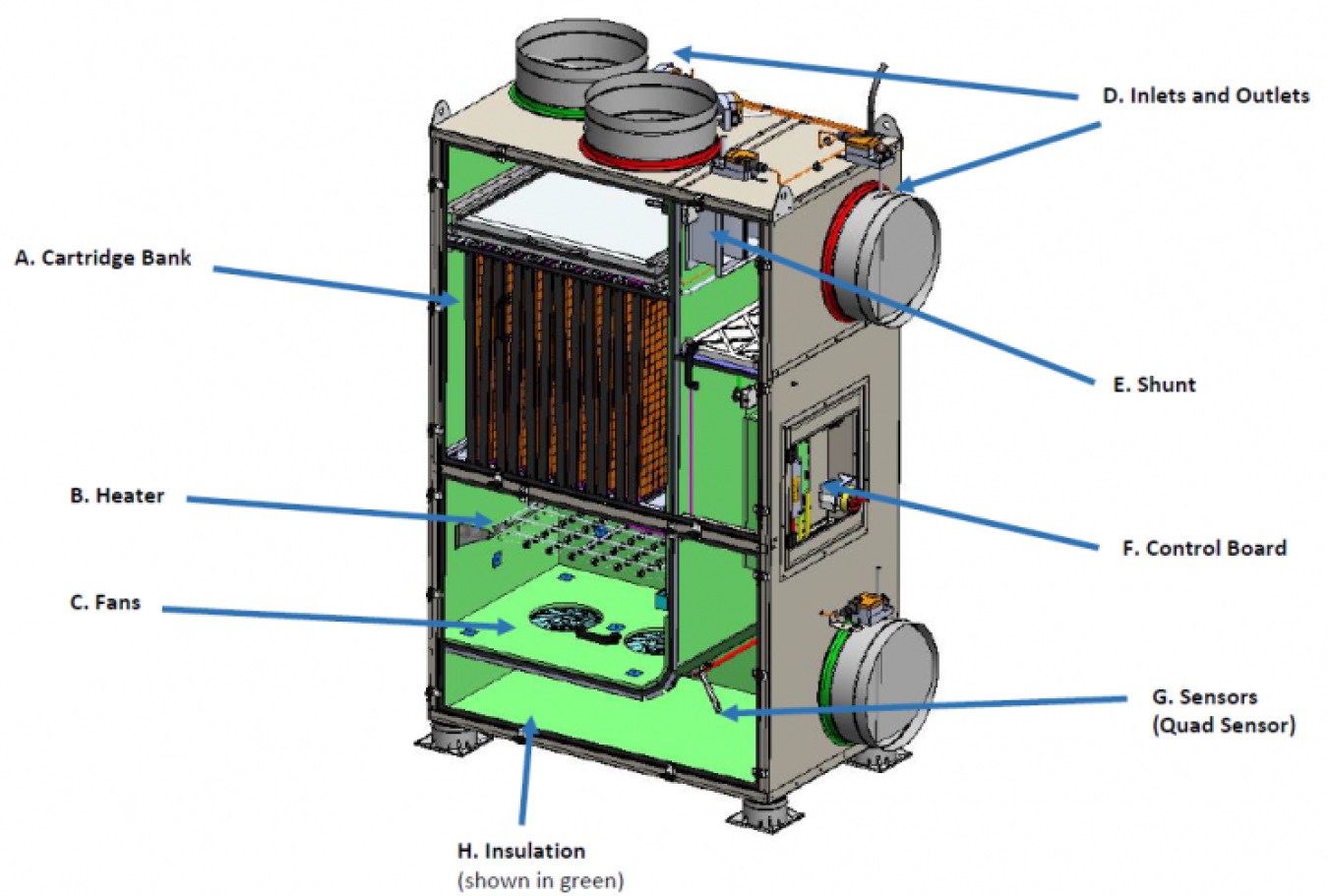
Johnson Controls Scrubber Unit.
Lead Performer: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory – Berkeley, CA
Partners:
-- BASF – Jessup, MD
-- Johnson Controls – Milwaukee, WI
-- United Technologies – Farmington, CT
-- Tsinghua University – Beijing, China
-- China Academy of Building Research – Beijing, China
-- China Merchants Shekou Industrial Zone Holdings Co. Ltd.
-- Shenzhen Institute for Building Research – Shenzhen, China
Project Term: April 1, 2016 – March 31, 2021
PROJECT OBJECTIVE
The U.S.-China Clean Energy Research Center (CERC) is a pioneering research and development (R&D) consortium bringing together governments, key policymakers, researchers, and industry to develop a long-term platform for sustainable U.S.-China joint R&D. Outdoor air ventilation for commercial buildings limits energy reduction opportunities and impacts indoor air quality because outdoor air must be thermally conditioned and the greatest amount of energy for conditioning is often needed during peak times. Additionally, outdoor air pollutants (e.g., particulate matter) increase indoors through ventilation.
The goal of this area of work is to develop and demonstrate technologies that manipulate air supply for energy-efficient heating, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) while providing excellent indoor environmental quality. Advances will be made to develop and demonstrate air cleaning technologies for fine particulate matter (PM2.5), ozone, formaldehyde, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and carbon dioxide (CO2); integrate air cleaning with ventilation by real-time monitoring using low-cost sensors; and develop simulation tools to aid system design and selection for different building types, climates, and air quality challenges. A study will also be conducted on indoor air pollutants in commercial buildings, and simulation tools will be developed to advance development, design and deployment for energy saving, air cleaning technologies. These simulation tools will include an air quality module integrated into EnergyPlus.
PROJECT IMPACT
This project will produce metrics and test conditions for air cleaning materials, simulation tools to advance deployment of air cleaning technologies for energy savings, and an air quality module integrated into Energy Plus. The energy savings potential of this project by 2030 are 0.56 Quads.
CONTACTS
DOE Technology Manager: Antonio Bouza
Lead Performer: Brett Singer and Hugo Destaillats, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory

