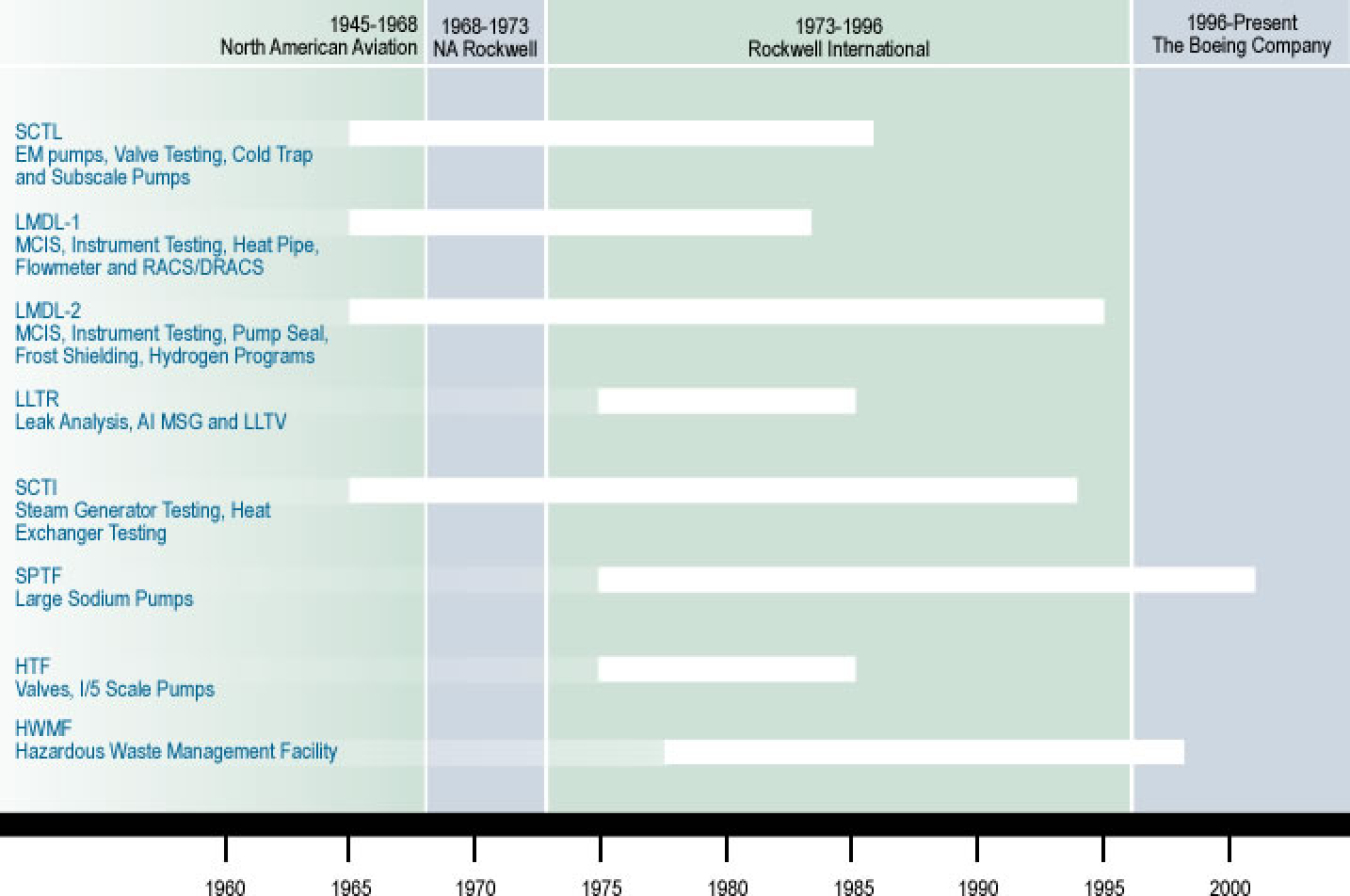
Select this picture to open a webpage with a timeline that provides more historical information about each program.
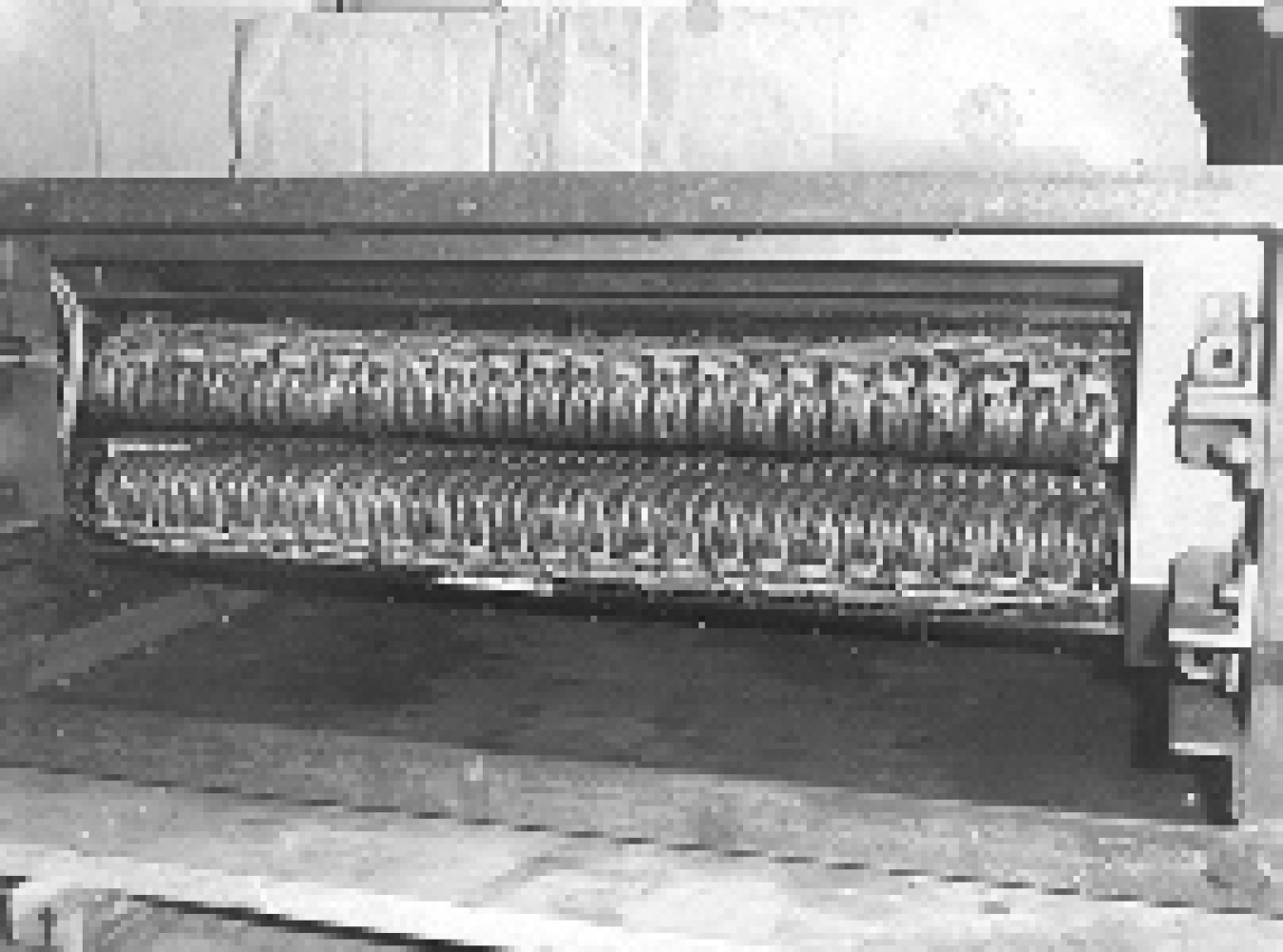
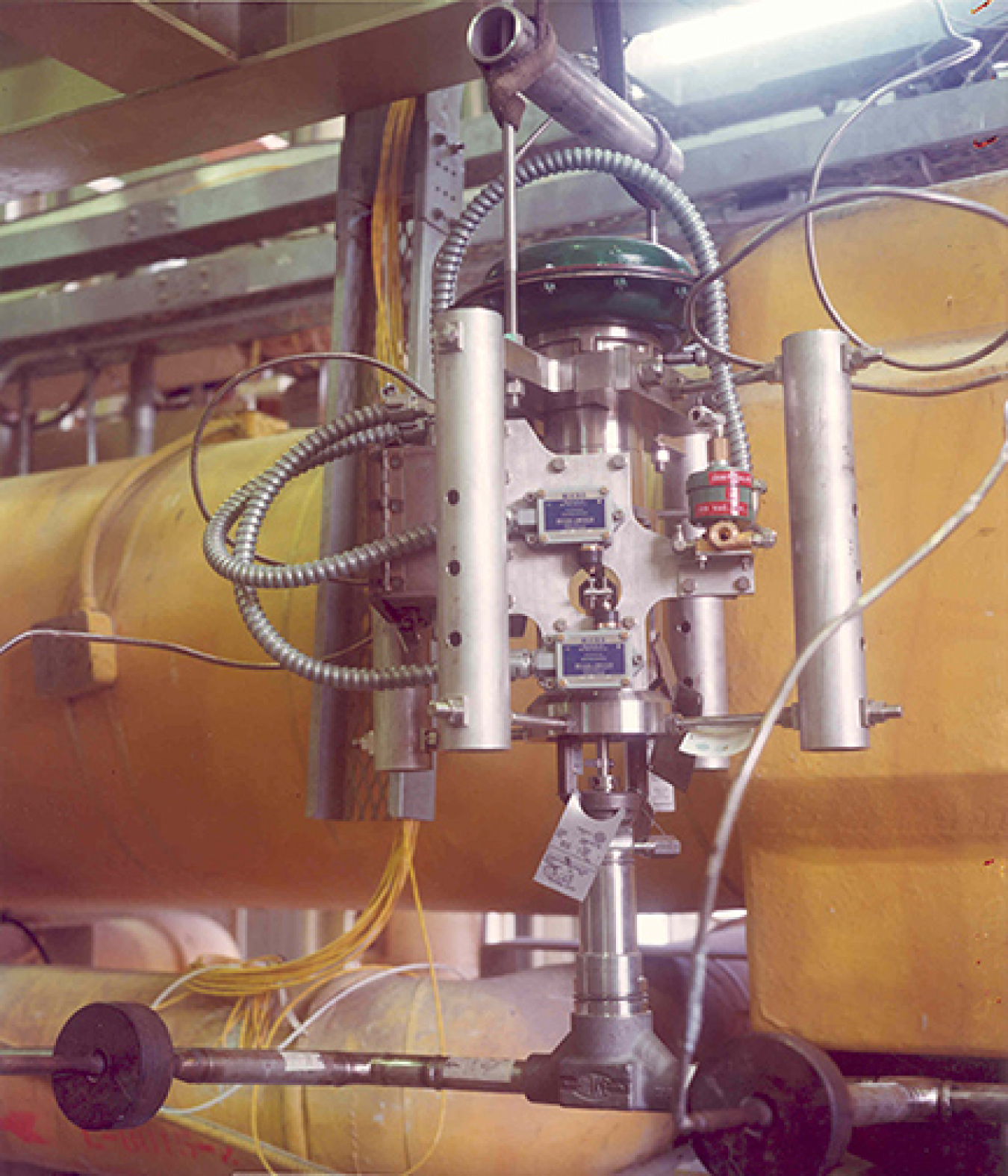
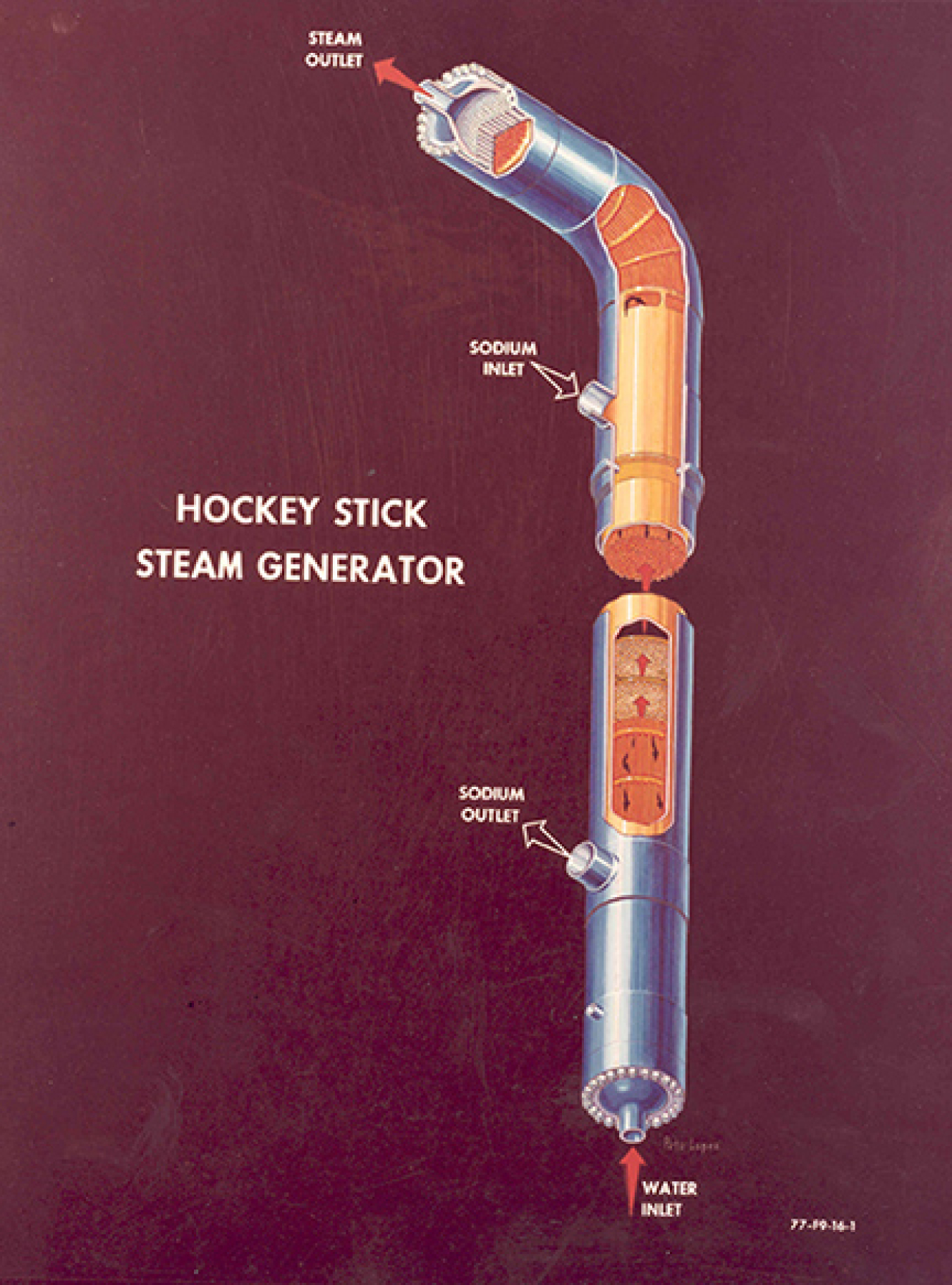
Throughout its existence, Area IV supported non-nuclear research and development programs. Primarily, these programs focused on testing liquid metal processes and developing liquid metal components (e.g., pumps, sodium water heat exchangers) and weld testing. This research supported the design of the Hallam Nuclear Power Facility, the Piqua Nuclear Power Facility, the Fast Flux Test Facility (FFTF) and the Clinch River Breeder Reactor. Liquid metal components were tested in a non-nuclear environment.
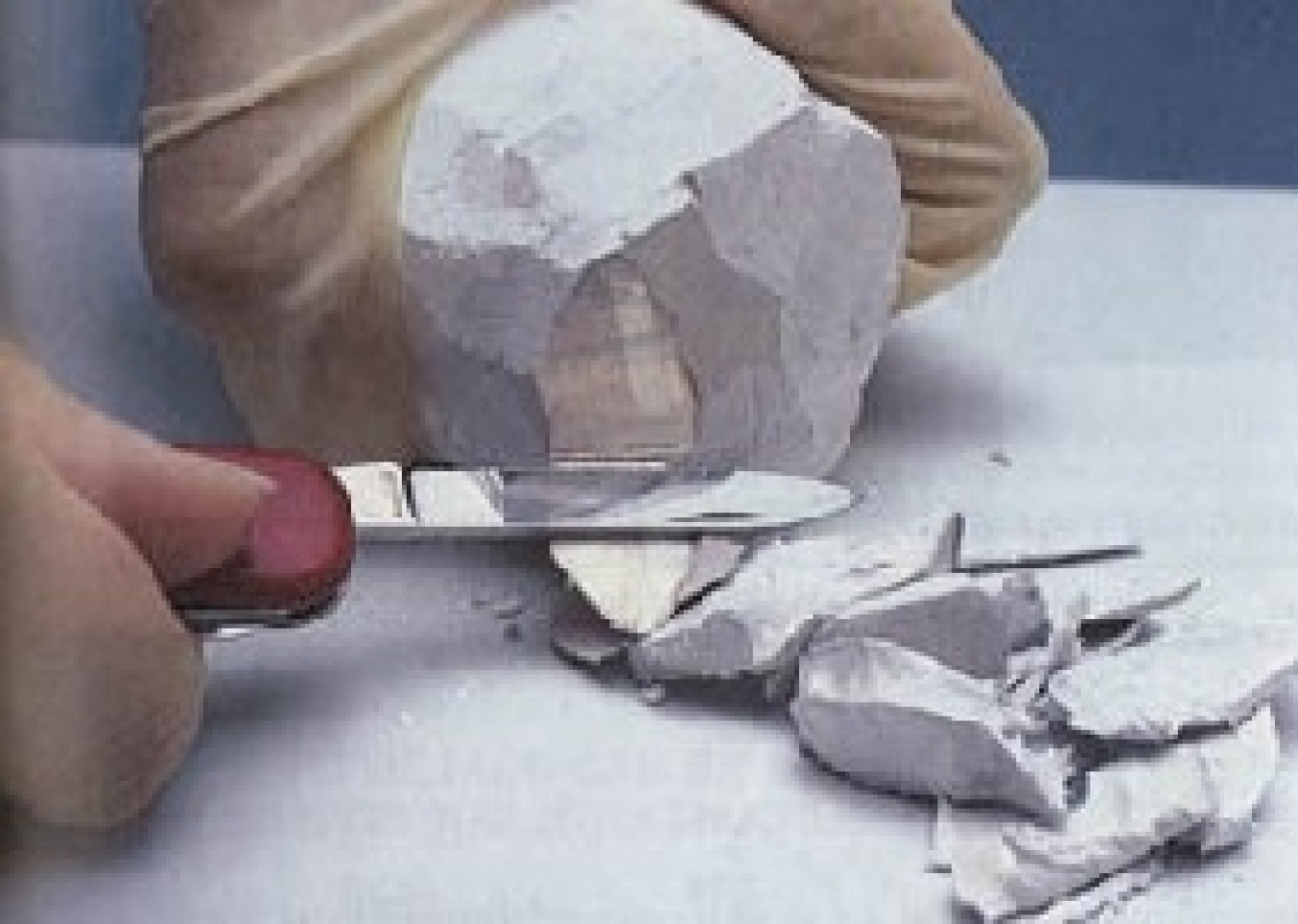

The research primarily involved metallic sodium. Sodium is a metal with a light gray appearance and, at room temperature, is as hard as cold butter. It is found in compound form in table salt; however, elemental sodium is not found in nature. Metallic sodium reacts with water, melts at 208°F and boils at 1618°F.
Sodium was chosen because:
- It has excellent heat transfer properties
- Has a low operating pressure when compared to water
- Has a low melting point
- It can be pumped using electromagnetic energy
In some nuclear reactors, the sodium is a cooling agent for the reactor's core. During the 1960's and the 1970's, experiments involving sodium included testing to support national efforts to develop nuclear power and liquid metal related technologies.
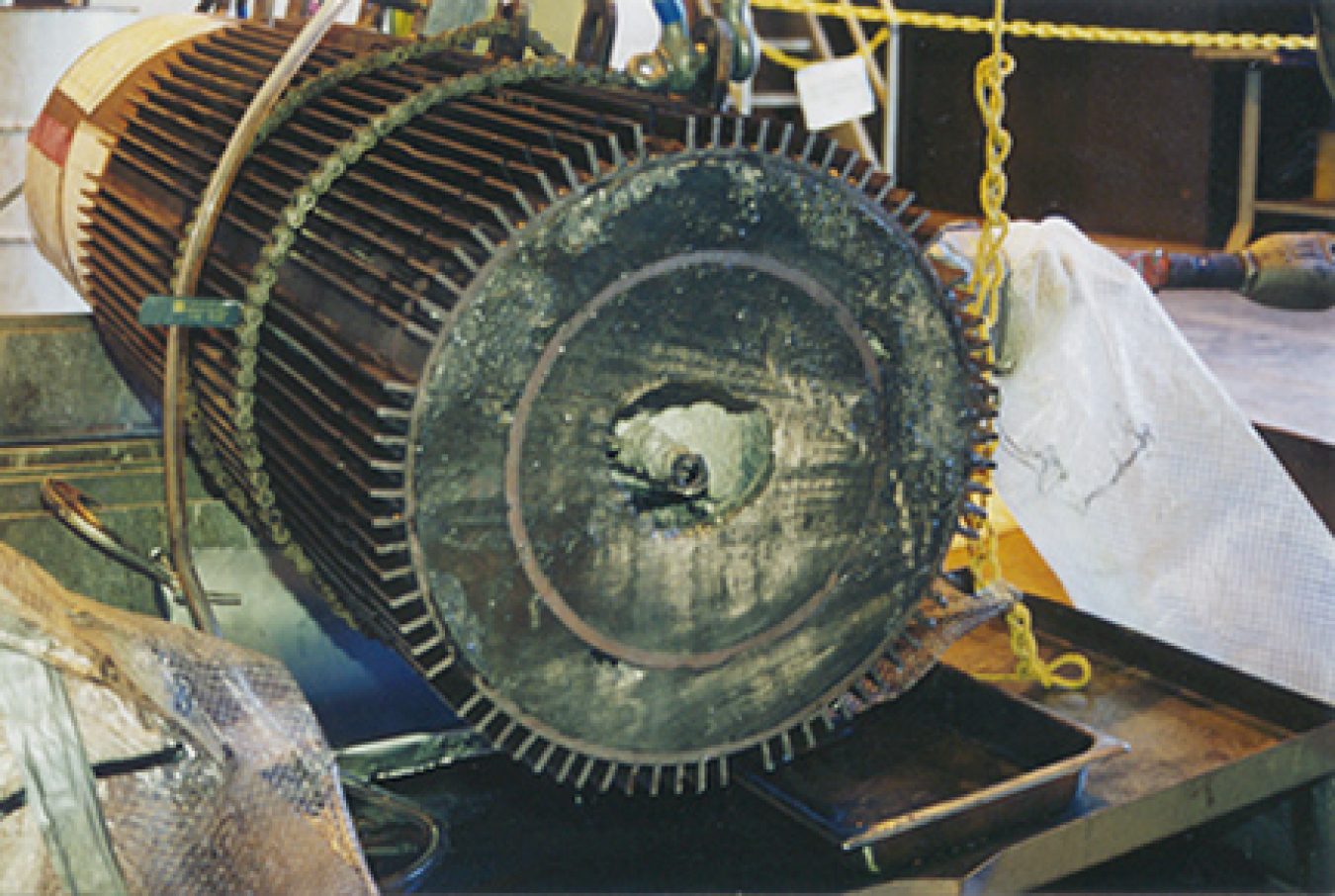
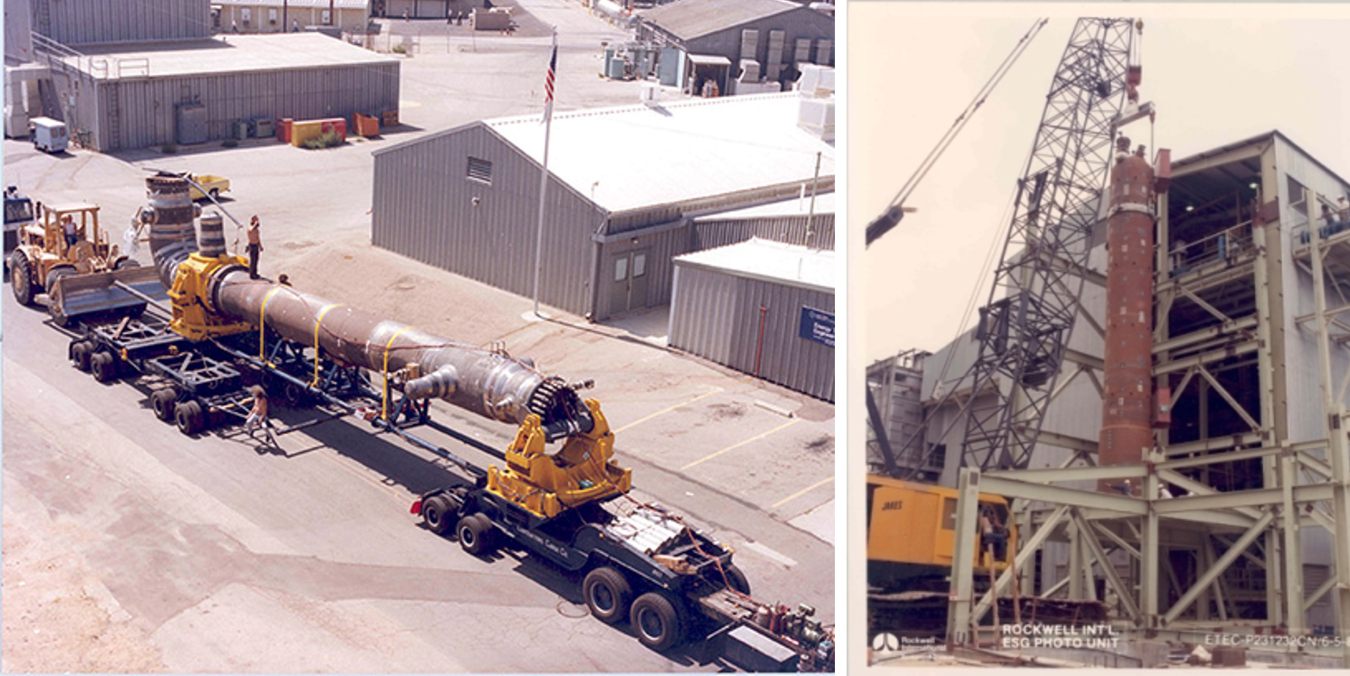



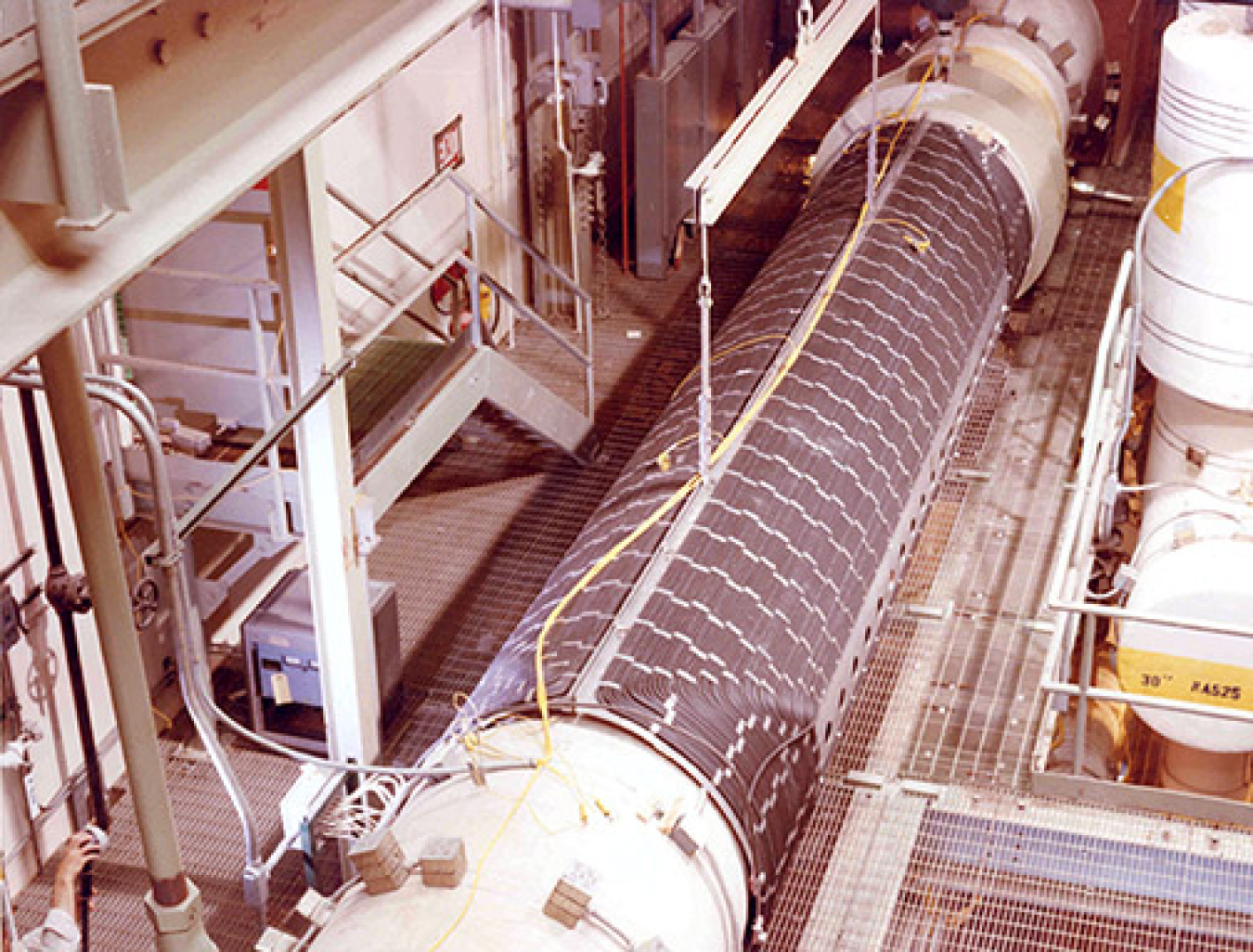
Evaluation of competing steam generator designs – The SCTI was used to test and compare competing engineering designs. The 75 megawatt stream generator on the left was designed by Atomics International while the similar sized unit on the right was designed by Babcox and Wilcox.