Absorption heat pumps are air-source heat pumps that use a heat source such as natural gas, propane, solar-heated water, or geothermal-heated water instead of electricity. Due to the common use of natural gas as a heat source, they are often called gas-fired heat pumps. There are also absorption coolers available that work on the same principle.
Key Points:
- Primary Uses: Mainly for industrial or commercial settings; suitable for large residential homes (4,000 square feet or larger).
- Heat Sources: Natural gas, propane, solar-heated water, geothermal-heated water.
- Technology: Utilizes ammonia-water absorption cycle for heating and cooling.
How Absorption Heat Pumps Work
Absorption heat pumps use an ammonia-water absorption cycle to provide heating and cooling. Similar to a standard heat pump, the refrigerant (ammonia) condenses in one coil to release its heat, then its pressure is reduced, and it evaporates to absorb heat. When the system absorbs heat from the interior of your home, it provides cooling; when it releases heat to the interior, it provides heating.
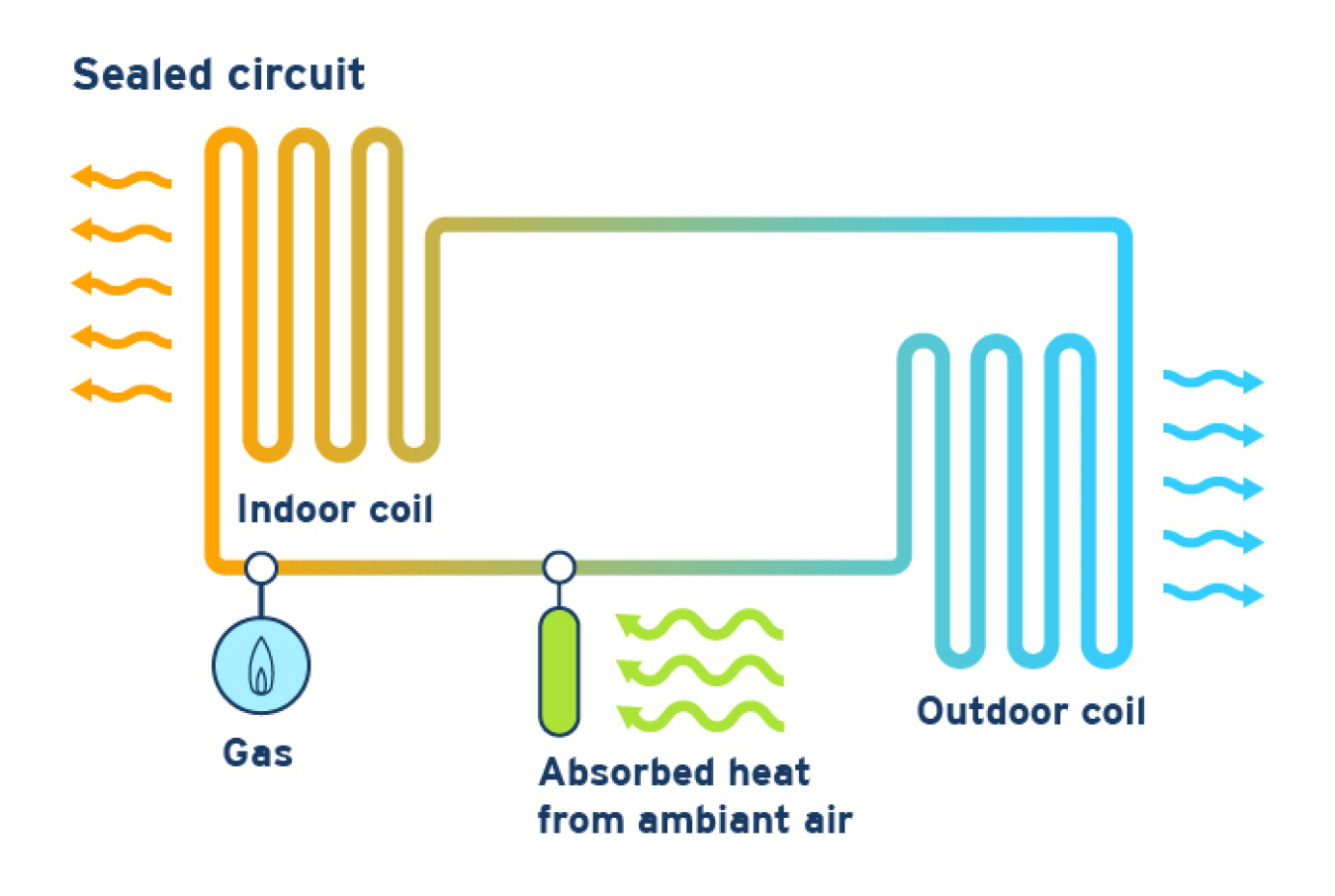
Key Components
- No Compressor: Instead of a compressor, the evaporated ammonia is absorbed into water. A low-power pump then increases the solution's pressure.
- Heat Source: The heat source boils the ammonia out of the water, restarting the cycle.
- GAX Technology: Generator Absorber Heat Exchanger (GAX) boosts efficiency by recovering heat released during ammonia absorption.
- Innovations: High-efficiency vapor separation, variable ammonia flow rates, low-emissions, variable-capacity combustion of natural gas.
Efficiency and Performance of Absorption Heat Pumps
The efficiency of air-source absorption coolers and heat pumps is indicated by their coefficient of performance (COP). COP is the ratio of either heat removed (for cooling) or heat provided (for heating) in Btu per Btu of energy input.
Benefits:
- Versatile Heat Sources: Can use solar energy, geothermal hot water, or other heat sources.
- Zoned Systems: Suitable for systems where different parts of the house are kept at different temperatures.
Applications in Large Residential Homes
Although absorption heat pumps have traditionally been used in industrial or commercial settings, they are now available for large residential homes. The 5-ton residential cooler systems currently on the market are appropriate for homes that are 4,000 square feet or larger.
Take Action
Ensure your system is installed correctly and maintained regularly to maximize efficiency and savings. If you have a large home and are considering an absorption heat pump, consult a qualified HVAC professional to determine the best system for your needs. For more information on energy-efficient heating and cooling solutions, visit the ENERGY STAR website.
Learn More About Heat Pumps
Subscribe to receive updates and energy-saving tips for consumers and homeowners.





